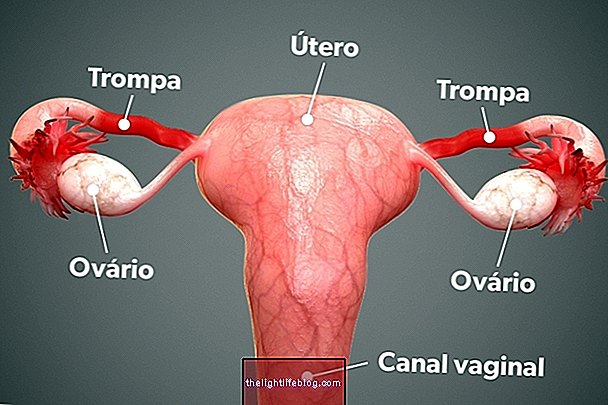
Kidney infection or pyelonephritis corresponds to a urinary tract infection in which the causative agent is able to reach the kidneys and cause inflammation, leading to symptoms such as renal colic, foul-smelling urine, fever and pain when urinating.
Kidney infection can be caused by infection by bacteria, such as E. coli, for example, fungi, mainly of the Candida species, and even some viruses. Kidney infection is usually the result of a bladder infection that lasts a long time and causes the micro-organisms that cause the infection to rise up to the kidneys, causing inflammation. In the case of chronic kidney infection, in addition to microorganism infection, the presence of lesions in the urinary organs or kidney stones can also cause the infection of the kidney.
Kidney infection should be diagnosed and treated as soon as it is discovered to prevent serious injury to the kidneys or lead to septicemia, where the micro-organism can reach the bloodstream and go to different parts of the body, causing infection and may even lead to death . Understand septicemia.
Symptoms of Kidney Infection
Symptoms of renal infection may appear suddenly and intensely, disappear within a few days (acute renal infection), or show no signs and symptoms, and the infection develops over time and, if untreated, may progress to renal failure (chronic renal infection).
The main symptoms of kidney infection are:
- Renal colic;
- Strong back pain;
- Difficulties in urinating;
- Willingness to urinate frequently and in small quantities;
- Pain or burning to urinate;
- Urine with bad smell;
- Fever;
- Chills;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting.
In the presence of any of these symptoms, the person should consult the urologist or nephrologist doctor, who will make the diagnosis of the disease through the evaluation of the symptoms. The doctor should also perform a physical examination, such as palpation and lumbar protrusion, and a urinalysis to check the presence of blood or white blood cells. See how the urine test is done.
Pregnancy kidney infection
Kidney infection in pregnancy is quite common and is usually a consequence of a prolonged infection in the bladder.
In pregnancy, increased levels of hormones, such as progesterone, leads to relaxation of the urinary tract, facilitating the entry of bacteria into the bladder, where they multiply and cause inflammation of the organ. In cases where the infection is not diagnosed or treated effectively, microorganisms continue to multiply and begin to rise in the urinary tract, reaching the kidneys and causing them to become inflamed.
Treatment of kidney infection during pregnancy can be done with antibiotics like Amoxicillin, which do not harm the baby. Learn how to cure urinary tract infection in pregnancy.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of kidney infection will depend on the cause of the infection and whether it is acute or chronic. In cases where the infection is caused by bacteria, the treatment consists of the use of antibiotics, such as Amoxicillin or Ciprofloxacin, for about 10 to 14 days. Some analgesics or anti-inflammatories are also indicated to relieve pain.
The most effective treatment for chronic kidney infections is to eliminate their causes. Some kidney infection remedies , such as antibiotics, can also be used to treat chronic kidney infection if there are signs of infection by bacteria.
During the treatment of kidney infection, the ingestion of large amounts of water is important to facilitate the cure of the disease.










.jpg)