Treatment for diphtheria is most often performed during hospitalization and should be started as soon as infection is suspected, especially in children, as it can lead to serious complications if not treated correctly.
The treatment is done with the objective of reducing the symptoms, being the results evaluated by the medical team from the observation of the decrease of the fever, of the swelling and improvement of the respiratory capacity.
Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae that leads to the appearance of grayish plaques in the throat, swelling of the neck, fever and sores on the skin. Get to know other symptoms of diphtheria and how the treatment is done.
How is the treatment done?
Diphtheria treatment can be done at home or during hospital stay, which happens most often, depending on the symptoms presented by the person. The treatment can take 1 month, varying from person to person, being more prolonged in children.
The treatment for diphtheria is established by the physician, and it is necessary to:
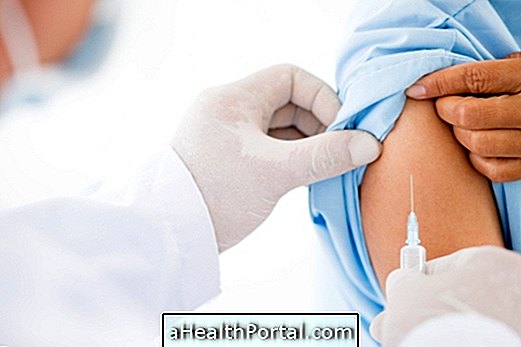
- Take an injection of diphtheria antitoxin, which has the function of decreasing the effects of the toxic substances released by the bacteria in the patient's body;
- Take antibiotics such as Penicillin, Erythromycin or Clindamycin, with the aim of eliminating the bacteria and preventing their transmission;
- Stay in an isolated room until the tests do not detect the presence of the bacteria, which can take up to 2 weeks. Isolation is important so that there is no contact with other people hospitalized;
- Intake large amounts of fluids to keep the body hydrated, especially in infants and children.
In addition, it is important to avoid straining and remaining at rest until the disease is resolved. When a person is having difficulty breathing, for example, a tracheostomy may be necessary, which is a surgical procedure where an opening is made in the neck to allow the person to breathe better, or put a respiratory tube in which oxygen is administered . Learn how to care for a person with a tracheostomy.
How is the prevention of diphtheria
Prevention of diphtheria is done through vaccination, which protects against tetanus and pertussis as well as protecting against diphtheria. This vaccine should be applied at 2, 4 and 6 months of age and should be strengthened at 4 and then every 10 years. Learn more about the diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis vaccine.
If the person has come in contact with a patient with diphtheria, it is important to go to the hospital for the injection of diphtheria antitoxin and thus prevent the spread and spread of the disease to others. Although it is more common in children, adults who do not have the current day vaccine against diphtheria or have a weakened immune system are more susceptible to Corynebacterium diphtheriae infection .

-o-que--sintomas-transmisso-e-tratamento.jpg)