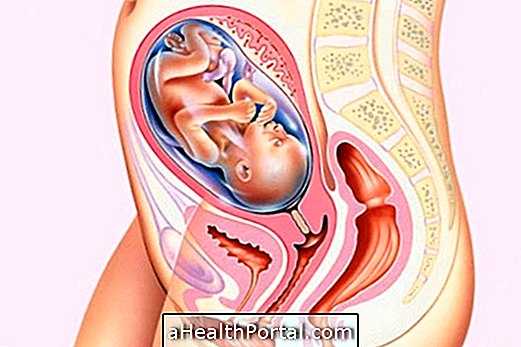
The causes of maternal and fetal death during childbirth are very variable and they usually occur in the case of a risky pregnancy or when a preterm birth occurs.
One of the most common causes of mother's death during childbirth is bleeding that can occur immediately after the baby leaves the uterus or in the first few days. Already, in the case of babies, those who are born very premature are those who are most at risk of life.
Maternal death can occur during delivery or up to 42 days after the baby's birth, with the most common causes being:
Causes of maternal death:
- Hypertension or Eclampsia;
- Postpartum haemorrhage;
- Infection;
- Abnormalities of uterine contraction;
- Unsafe abortion;
- Complications of diseases preexist or have developed during gestation.
Causes of fetal death:
Causes of fetal death at birth or within the first 28 days of birth may be:
- Placental insufficiency;
- Lack of oxygen in the baby due to winding in the umbilical cord, for example;
- Fetal malformation;
- Extreme prematurity.

How to reduce the risk of death at childbirth
The best way to achieve a healthy pregnancy so that the baby can develop and be healthy is to ensure that the woman has the necessary assistance during her pregnancy. To do this you must:
- Prenatal follow-up from the beginning of pregnancy to the time of delivery;
- Perform all the necessary examinations during prenatal care;
- Eat well, betting on healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, vegetables, cereals, grains and lean meats;
- Only do physical exercise when accompanied by a qualified professional;
- Control any existing disease by performing examinations and following the treatment proposed by the physician;
- If you know about delivery and if you choose normal delivery, prepare yourself physically for it to try to reduce labor time;
- Do not take medicines without medical advice;
- Avoiding excessive weight gain in pregnancy because cardiac changes increase the risk of death at birth;
- Keep diabetes well controlled every day;
- Prevent the woman from becoming pregnant again in a period of at least 1 year;
- Supplementation of iron and folic acid during pregnancy to prevent fetal malformation.
The risk of maternal and fetal death has declined year after year in Brazil and worldwide due to pre-natal and modern means of diagnosis and treatment currently available, but women who do not receive adequate follow-up during pregnancy and have a higher chance of complications.