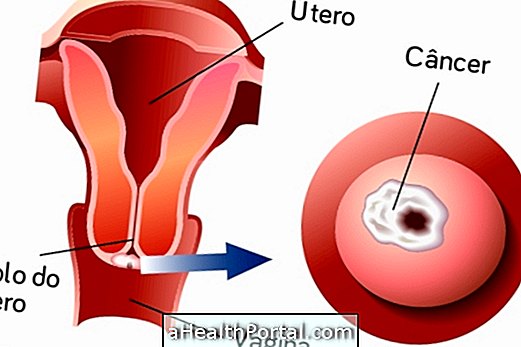
There may be several causes of pain in the foot of the belly, and it is usually related to organs such as the uterus, bladder or intestine, and the pain may begin at another location and be irradiated to the foot of the belly.
Because there are several causes, it is very important to make the correct diagnosis so that the treatment is effective and adapted to each case.

1. Changes in intestinal transit
Changes in intestinal transit such as diarrhea, constipation or gas can cause abdominal pain and may arise from a variety of factors such as food intolerances to lactose or gluten, eg gastroenteritis or viruses, or after increased intake of some foods that produce gas, such as milk, cauliflower and cheese, for example.
How to treat
To treat diarrhea faster one should avoid greasy foods, eggs and milk, one should take black tea or chamomile or opt for a probiotic, such as Floratil or Repoflor, for example.
Already to treat constipation and gas it is recommended to make a high fiber diet, drink lots of water, avoid carbohydrate foods such as rice, potatoes and white bread, or do an abdominal massage below the navel, in the right direction to to the left. Fennel tea can also be a natural option to end gas fast. Learn more helpful tips and watch the following video to learn how to eliminate the gases:

2. Poor digestion
Poor digestion can also cause pain and swelling in the back of the belly, as well as other symptoms such as heartburn, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation.
How to treat
The treatment of bad digestion can be done by choosing foods that are easy to digest and do not irritate the stomach, such as gelatin, fruit juices, bread and unpretentious cookies, and avoiding the consumption of liquids during digestion.
You can also choose to use medicines obtained at the pharmacy like Gaviscon or milk of magnesia, or by the use of home remedies like tea of boldo or tea of fennel, for example. See more ways to treat bad digestion.
3. Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection is usually caused by bacteria from the gut that enter the urinary system and is therefore more common in women due to the proximity of the anus to the urethra. Symptoms vary with the person, but pain usually arises when urinating, and if the infection reaches the bladder, you may smell bad, blood in the urine and abdominal pain or feeling of heaviness in the bladder.
How to treat
The most commonly used remedies for the treatment of urinary tract infection are antibiotics, such as Fosfomycin and Amoxicillin, and analgesics such as Pyridium or Uristat, for example. These medicines should always be advised by the doctor. See more about treating urinary tract infection.

4. Stone in the kidney
The kidney stone, when it is not eliminated in the urine, can get stuck in the channels through which the urine passes, generating very intense pain and sometimes blood in the urine. This intense pain is usually felt in the back, but may also reach the bottom of the belly, groin or testicles.
How to treat
Treatment consists of administering an analgesic such as Paracetamol, Buscopan or Tramadol, for example, in addition to drinking lots of water, reduce the salt content in food and rest.
In less severe cases, one can also opt for a natural treatment, using a rock break tea, due to its diuretic action and facilitating the elimination of stones. Learn how to make this tea.
5. Menstrual cramps
Also known as dysmenorrhea, menstrual cramps can cause severe pain in the back of the belly and back, discomfort and discomfort in the woman, and if they are very intense, a gynecologist should be consulted in order to identify if there is any dysfunction of the reproductive organs.
How to treat
There are several ways to cushion menstrual cramps, such as using contraceptive, or anti-inflammatory and analgesic like Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
In addition, you can also use other techniques such as doing exercises that help reduce cramps by lying down on your belly and bringing your knees to your chest, holding your legs with your hands, applying warm water compresses to the abdomen, or even practicing physical exercise. Learn more tips to reduce menstrual cramps.

6. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, causing severe abdominal cramps during menstruation, which may increase over time. However, the disease is only discovered later, especially when the woman can not get pregnant.
How to treat
Women who wish to have children can treat endometriosis through the use of oral contraceptives, hormonal drugs such as Zoladex, for example, by placing an intrauterine device or undergoing surgery to remove the outbreaks of endometriosis. In cases of women who do not wish to have children, surgery can be performed in which the endometrial tissue and the involved organs are removed. See how surgery for endometriosis is done.
7. Ovarian cysts
The cyst in the ovary consists of a pocket of fluid that forms in or around the ovary and may or may not compromise the pregnancy. Cyst in the ovary can cause pain in the pelvic region and during sexual intercourse, delayed menstruation, bleeding, nausea and vomiting and excessive tiredness. Here's how to identify the cyst in the ovary.
How to treat
Treatment may vary depending on the type of cyst the woman has, and can be resolved only with the change of contraceptive, or in more severe cases, to resort to surgery.

8. Pregnancy
One of the early symptoms of pregnancy are abdominal cramps and bloating due to an increase in blood flow in the pelvic region and due to pelvic changes that are happening. Also, around 7 weeks of gestation, the underside of the navel begins to get hard.
How to treat
When pregnant belly pain develops, it is recommended to drink liquids, foods of easy digestion, to eat small amounts and to avoid ingesting foods rich in fibers like cereals, fruits in shell or leguminosas, for example. However, if the pain is very intense you should go to the doctor. See more foods to help treat tummy ache in pregnancy.
9. Ectopic pregnancy
Although pain in the foot of the belly is common in pregnancy, if it becomes very intense, it may be caused by an ectopic pregnancy, which occurs when the embryo develops outside the uterus and can cause severe abdominal pain on one side only, abdominal swelling and loss of blood through the vagina. Learn what causes ectopic pregnancy.
How to treat
Treatment depends on the location of the embryo, but can be done with the use of medicines to cause abortion, or surgery can be done to remove the embryo and rebuild the uterine tube, for example.
10. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
This disease is characterized by an infection that begins in the vagina or cervix, and reaches the endometrium, fallopian tubes and ovaries, may take only a few days or if it is chronic, it may persist for months or even years. This can be a sexually transmitted disease or be related to endometriosis.
In addition to causing pain in the bottom of the belly, fever, vaginal bleeding, white or yellow discharge, and pain during intimate contact may also occur. Learn more about pelvic inflammatory disease.
How to treat
Treatment involves the use of antibiotics for about 14 days. During treatment, close contact should be avoided, and if an intrauterine device is used, it should be removed.

Inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia is more common in men and consists of a lump in the groin area caused by passage of a part of the intestine through a weaker point of the abdominal muscles, causing pain and discomfort in the region when doing some movements such as getting up or to bow.
How to treat
The best form of treatment for inguinal hernia is surgery, where the portion of the intestine is placed back in place and the abdominal wall is strengthened. This surgery is usually short and quick to recover. See what the surgery consists of and how recovery is done.
12. Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion is a problem that usually occurs in young men when a testicle twists around the spermatic cord, decreasing blood circulation, and can cause serious lesions in the testis. The most common symptoms are intense pain in the testicles, with swelling and increased sensitivity in the scrotum and pain in the belly or groin. See more symptoms of testicular torsion.
How to treat
The treatment should be done as soon as possible in the hospital, with surgery, to place the testicle in the correct place and thus allow the passage of blood, avoiding death of the organ.