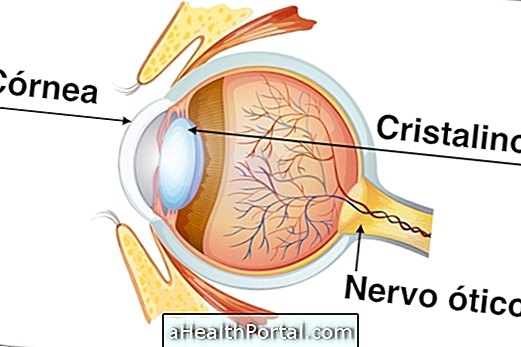
Corneal transplantation, the transparent membrane that lines the eye, is a surgery to replace the cornea with a healthy one that allows good vision. The surgery is performed in the SUS and it is not always necessary to remove the stitches from the surgery, which are not visible.
In the postoperative period of corneal transplantation, the individual will have a dressing on the eye that should only be removed by the physician 2 days after the procedure. During this period you should avoid making efforts and eating healthy, drinking enough water to keep the body and the new cornea well hydrated.
In the consultation the doctor will remove the dressing and the person can see, although the vision is still a bit blurry initially, gradually it becomes cleaner.
8 Essential post operative care
Care after corneal transplantation is very important to avoid rejection and possible complications. Therefore it is recommended:
- Stand with your eyes closed during the 1st day;
- Do not wet the bandage;
- Use eye drops and medicines prescribed by the doctor;
- Avoid rubbing the operated eye;
- Use acrylic sleeping protection to not apply pressure to the eyes;
- Wear sunglasses when exposed to the sun and also indoors when the lights are on;
- Avoid physical exercise the first week after transplantation;
- Sleep for the opposite side of the operated eye.
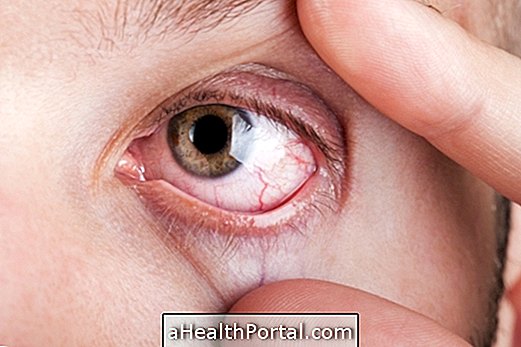
During the corneal transplant recovery period, the individual should be alert for signs of corneal rejection, such as red eye, eye pain, decreased vision, or excessive sensitivity to light.
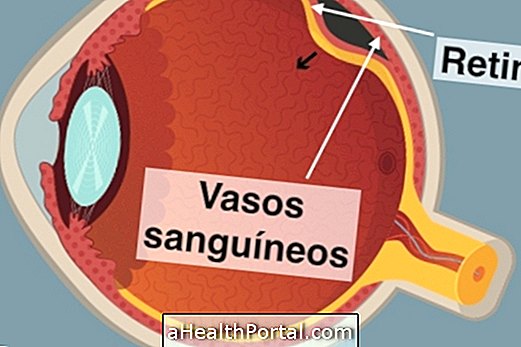
As with any other surgery, complications can occur that can impair vision such as inflammation, infection, bleeding, retinal detachment. It can also happen the rupture of the points and swelling of the cornea and so if presenting some symptom should seek the doctor.
Signs of transplant rejection

Corneal transplant rejection can occur in anyone who has undergone transplantation and although it is more common in the first few months after surgery, rejection can occur even 30 years after the procedure.
Signs that may indicate rejection may be observed 14 days after transplantation and are:
- Redness of the eyes;
- Photophobia - difficulty in keeping your eyes open in very bright places or in the sun;
- Blurred or blurred vision;
- Pain in the eyes.
Some situations that increase the risk of rejection are a previous transplant that was rejected by the body, when the individual is young, there are signs of ocular inflammation, glaucoma or herpes, for example.
To reduce the risk of rejection, the ophthalmologist usually indicates the use of ointment-like corticosteroids, such as 1% prednisolone acetate, to apply directly to the transplanted eye and immunosuppressive drugs.
When corneal transplantation is indicated
Corneal transplantation may be indicated for the treatment of diseases related to corneal transparency, such as:
- Keratoconus;
- Leukoma;
- Ocular herpes;
- Bullous keratopathy;
- Leukoma.
Generally, corneal transplantation is done under general and ambulatory anesthesia, requiring fasting 6 hours before surgery.
Who can be a donor of cornea
Anyone between 3 and 70 years of age can be a donor of cornea after his death and just communicate their family members from the moment they wish. However, the removal of the corneas of the person is only done when a person in charge of the family signs a document in the hospital allowing their removal.
Removal of corneas is not indicated when the individual has the HIV virus, leukemia, generalized infection or when the cause of death is unknown.