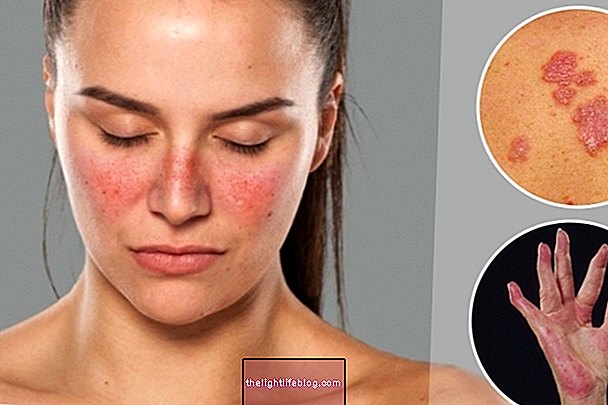
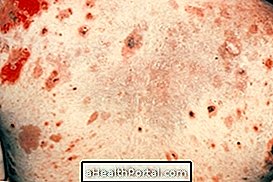
Dermatitis herpetiformis, also known as Duhring's disease or celiac dermatitis herpetiformis, is an autoimmune disease, which causes the formation of small blisters on the skin that itch, similar to herpes lesions.
Although this disease may appear in any person, it is more common in people suffering from celiac disease, as it seems to be related to the sensitivity to gluten.
Dermatitis herpetiformis has no cure, but treatment with a gluten-free diet and antibiotic use, in the most severe cases, helps alleviate symptoms, allowing better quality of life.

Main symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of dermatitis herpetiformis include:
- Red plaques with peeling;
- Small blisters that itch;
- Bubbles that burst easily when scratching;
- Burning sensation in affected regions.
In addition, it is also very frequent the appearance of wounds around the blisters, which arise from scratching the skin very intensely.
The regions most affected usually are the scalp, butt, elbows, knees and back and usually appear symmetrically, ie appears on both elbows or both knees, for example.
What causes dermatitis herpetiformis
The possible cause of dermatitis herpetiformis is intolerance to gluten, because this substance activates the immune system, giving rise to the formation of immunoglobulin A, a substance that causes the body to attack the cells of the intestine and skin.
Although it appears to be caused by gluten, there are many cases of people with dermatitis herpetiformis that do not present any intestinal symptoms of gluten intolerance and therefore the cause has not yet been fully defined.
How is the treatment done?
The most commonly used form of treatment to combat dermatitis herpetiformis is to eat a gluten-free diet, so wheat, barley and oats should be eliminated from the diet. Check out more guidelines on how to remove gluten from food.
However, as the diet takes some time to take effect, the dermatologist may also indicate the use of an antibiotic tablet, known as Dspsone, which relieves symptoms in 1 to 2 days. Because Dapsone can cause several side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea and even anemia, the dose of Dapsone should be decreased over time until the minimum dose is found to be able to relieve the symptoms.
In the case of an allergy to Dapsone, the dermatologist may prescribe the use of ointments with corticosteroids or the use of other antibiotics, such as Sulfapyridine or Rituximab, for example.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually made with a biopsy of the affected skin, in which the doctor removes a small piece of skin that will be evaluated in the laboratory to assess if the presence of immunoglobulin A is present at the site.