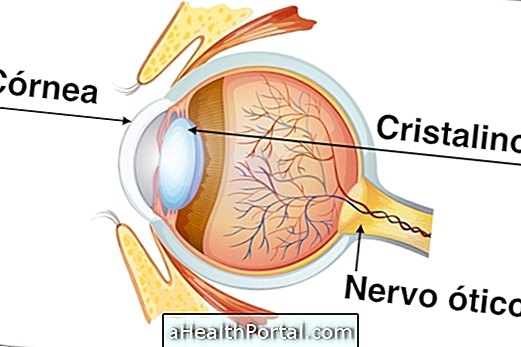
The ophthalmologist, popularly known as an ophthalmologist, is the doctor who specializes in evaluating and treating vision-related diseases, involving eye and its attachments, such as tear duct and eyelids. Some of the diseases most treated by this specialist are myopia, astigmatism, farsightedness, strabismus, cataracts or glaucoma, for example.
The ophthalmologist performs consultations, which may be private or through the SUS, in which the ophthalmological examination, vision tests are performed, as well as examinations, the use of glasses and medications to treat vision, and the ideal is done an annual visit to assess eye health. See how the ophthalmic examination is done and what tests can be done.

When To Go To The Ophthalmologist
The ophthalmologist should be sought whenever there is any change in visual ability or eye symptoms. However, even without symptoms, regular follow-up is necessary for the early detection and treatment of changes that commonly appear in lifelong vision.
1. Children
The first test of vision is the eye test, which can be done by the pediatrician to detect early vision diseases in the baby, such as congenital cataract, tumor, glaucoma or strabismus, and if changes are detected, it is necessary to start the ophthalmologic follow-up.
However, if there is no change in the eye test, the first visit to the ophthalmologist should be performed between three and four years of age, when it is possible to examine better and the child can better express the visual difficulties.
Thereafter, even if no alterations to the ophthalmologic examination are detected, consultations can be made at intervals of 1 to 2 years to follow the child's visual development, and the appearance of changes such as myopia, astigmatism and hyperopia, for example, which can disrupt learning and performance in school.
2. Teenagers
At this stage the visual system develops rapidly, and changes such as myopia and keratoconus may appear, so regular eye exams are required about once a year or whenever there are visual changes or difficulty in reaching school at school, due to symptoms such as visual fatigue, blurred vision, headaches.
In addition, makeup and contact lenses, which can cause eye allergies, or contact with infectious agents, can cause conjunctivitis and stye.
It is also common for teenagers to be exposed to both the UV radiation of the sun without proper protection with quality sunglasses and the computer screen and tablet, which can be harmful to eyesight. Learn what is computer vision syndrome and what to do to avoid it.

3. Adults
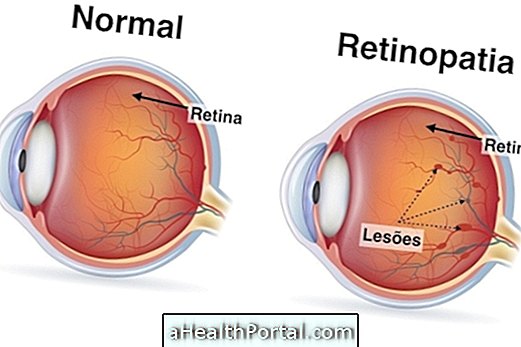
From the age of 20 onwards, diseases that compromise the retina can begin to appear, which can happen due to circulatory or degenerative problems, especially if there are unhealthy habits such as smoking and irregular treatment of diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Thus, if symptoms such as blurred vision, loss of central or localized vision in another region, or difficulty seeing at night, it is important to seek care with the ophthalmologist for specific evaluations.
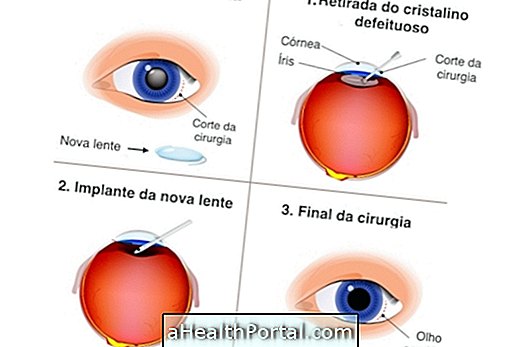
In adulthood it is also possible to do some cosmetic or refractive surgeries, such as LASIK or PRK, which help to correct visual changes and decrease the need for degree glasses.
In addition, after the age of 40, it is important to keep visiting the ophthalmologist annually, since other changes may occur during this time due to the advancing age, such as presbyopia, known as tired eyesight and glaucoma. Check out the risk of developing glaucoma and how to identify it soon.
4. Elderly
After the age of 50, and especially after age 60, it is possible that vision problems, such as cataracts and macular degeneration, may develop and can be treated correctly to avoid blindness. Learn about age-related macular degeneration and how to protect yourself.
Thus, it is important to keep the annual consultation to the ophthalmologist, so that these diseases are detected as soon as possible, allowing an effective treatment. In addition, it is important that the vision is well corrected in the elderly, because changes, even if small, can lead to the sensation of imbalance and risk of falls.