The cytology test is the analysis of fluids and secretions of the body, through the study of the cells that make up the sample under the microscope, being able to detect the presence of signs of inflammation, infection, bleeding or cancer.
This test is usually indicated to examine the contents of cysts, nodules, unusual fluids that accumulate in body cavities or abnormal secretions such as sputum. Some of the main types of cytology are those performed in the aspiration of thyroid or breast nodules, as well as in the pap smear or in the aspirate of respiratory secretions, for example.
Although the cytology examination can evaluate several types of changes, it is called oncotic cytology when it specifically investigates the presence of cancer cells.
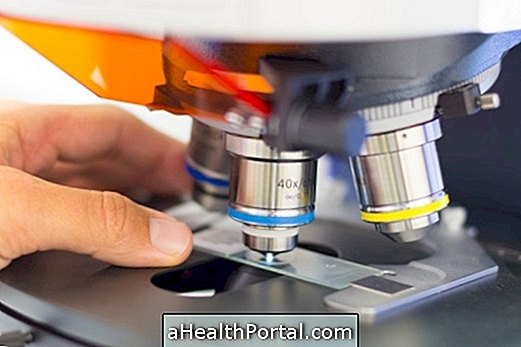
It should be remembered that cytology and histology are different examinations, because the cytology evaluates the characteristics of the cells present in a material, generally obtained by a puncture, while the histology studies whole pieces of tissues, being able to observe the composition and architecture of the material, being usually collected by a biopsy, and is usually more precise. Check what the biopsy is and what it is for.
Main types
Some examples of cytology tests are:
1. Thyroid aspiration cytology
Thyroid needle aspiration cytology (FNA) is a very important test to evaluate thyroid nodules and cysts because it can indicate whether it is a benign or malignant lesion.
In this examination, the doctor will puncture the nodule, being able to be guided by the ultrasonography, and to obtain samples of the cells that compose it. Then the material is placed on a slide for analysis under a microscope, and it can be seen if the cells have anomalous characteristics that may suggest cancer.
In this way, aspiration cytology is useful to guide the best treatment for a nodule, indicating the need for only follow-up, in benign cases, surgery to remove the thyroid in cases suspected of malignancy, as well as chemotherapy if identified the cancer.
Learn more about when this test is needed and how to understand the results in Thyroid Punch.
2. Breast aspiration cytology
Breast aspiration is one of the most frequent types of cytology and very important for evaluating characteristics of cysts or breast lumps, especially when they grow rapidly or have suspicious characteristics of cancer. Understand the risk of breast cancer being cancer.
As with thyroid puncture, the examination can be guided by ultrasonography or not, and then the material is sent to the laboratory for the cytology examination to evaluate the cells that make up the aspirated material.

3. Papanicola examination
In this examination scrapes and brushes of the uterine cervix are made to collect samples of cells from this region, which will be fixed on a slide and sent to the laboratory.
Thus, this test is able to identify vaginal infections, STIs and signs of cervical cancer. Cancer cell research is also known as oncotic cytology of the uterine cervix, and this test is very important for the early diagnosis and prevention of cervical cancer.
Check out how the pap smear is done and understand the results.
4. Cytology of respiratory secretions
Respiratory secretions such as sputum from the lungs or nasal mucus can be collected, usually by aspiration, to be evaluated in the laboratory. This type of test is often asked to try to identify the microorganism that causes an infection, such as fungi or bacteria, such as tuberculosis bacillus, for example. In addition, it can also assess the presence of cancer cells, blood or signs of allergy.
5. Cytology of body fluids
Several other types of fluid and body fluids can be evaluated in the cytology examination, and a frequent example is the urine cytology when looking for infections or inflammations of the urinary tract.
Another important example is the cytology of ascitic fluid, which is a fluid that accumulates in the abdominal cavity mainly due to abdominal diseases such as cirrhosis. This test may be asked to clarify the cause of ascites, as well as to look for infections or even signs of abdominal cancer. Learn more about this problem in what is ascites.
The fluid that accumulates in the pleura, which is the space between the membranes lining the lungs, in the pericardium, which is the membrane surrounding the heart, or even the fluid that accumulates in the joints, can also be collected for cytology. arthritis caused by autoimmune or infectious diseases, for example.