Plasmapheresis is a type of treatment used mainly in case that diseases that occur with the increase of substances that can become harmful for the organism, like proteins, enzymes or antibodies, for example. Thus, plasmapheresis can be recommended in the case of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Myasthenia Gravis, which is an autoimmune disease characterized by the progressive loss of muscle function due to the production of autoantibodies.
This procedure aims to remove the substances present in the plasma by means of the filtration process. Plasma accounts for about 10% of blood and consists of proteins, glucose, minerals, hormones and clotting factors, for example. Learn more about blood components and their functions.
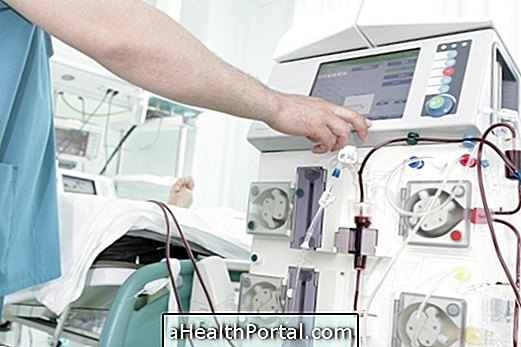
How is it done?
Plasma corresponds to the liquid part of the blood and is made up of proteins, such as albumin and antibody, in addition to glucose, minerals and coagulation factors. Some diseases occur with the increase of some of the constituents of the plasma, which makes plasmapheresis an efficient type of treatment in these cases.
Plasmapheresis is a procedure that aims to filter the blood by removing the substances that are present in the plasma and returning to the body plasma without the substances that are causing or giving continuity to the disease. This treatment is done in a machine, similar to hemodialysis, in which the patient's blood is withdrawn and the plasma separated. The plasma undergoes a filtration process, in which the substances that are present are removed and the plasma free of substances is returned to the body.
This procedure, however, filters all the substances present in the plasma, both beneficial and evil. Therefore, the same volume of beneficial substances that is removed is replaced by the use of a fresh plasma bag provided by the hospital blood bank, avoiding complications for the person.
Plasmapheresis is done by means of a catheter that is placed in the jugular or femoral way and each session lasts in average 2 hours, being able to be done daily or on alternate days, according to the doctor's orientation. Depending on the disease being treated, the doctor may recommend more or fewer sessions, and 7 sessions are usually indicated.
Although plasmapheresis is a very effective type of treatment, it is important that the person continues to make the medical treatment indicated by the doctor, as doing this does not prevent the production of the substances related to the disease. That is, in the case of autoimmune diseases, for example, plasmapheresis is responsible for the removal of autoantibodies, avoiding greater damages to the organism, however the production of these antibodies is not paralyzed, and the person must use immunosuppressive drugs of according to your doctor's advice.
Possible Complications
Plasmapheresis is a safe procedure, but just like any other invasive procedure, it has risks, such as the occurrence of hematoma or infection at the site of venous access, and it is important that it be done by a trained professional and that it respects the hygiene conditions related to patient safety. In addition, due to the removal of the coagulation factors present in the plasma, there may be greater risks of bleeding, which can be avoided by using the fresh plasma bag.
It is also possible to have transfusion reactions, such as the allergic reaction to proteins present in the plasma that has been transfused.
What is it for
Plasmapheresis is a type of treatment that can be indicated by the doctor in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, such as Lupus and Myasthenia Gravis, because in these cases there is a large production of antibodies that act against the body itself, resulting in the onset and progression of the disease. disease.
In addition, this procedure may be indicated in the treatment of Multiple Myeloma, Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia, Guillain-Barré Syndrome, Multiple Sclerosis, and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, in which excess antibody may be interfering with the coagulation process. Learn more about PTT.