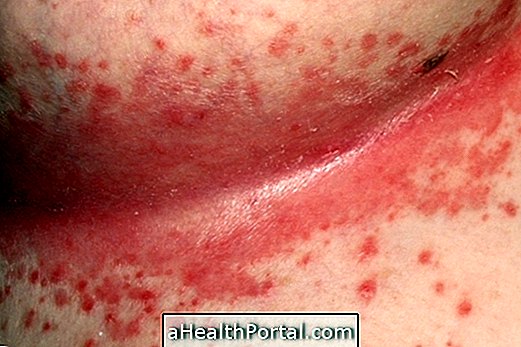
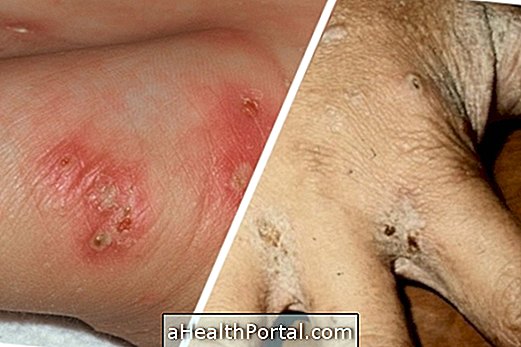
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease, of unknown cause, characterized by inflammation in various parts of the body such as lung, liver, skin, and eyes, as well as the formation of anus, resulting in excessive tiredness, fever or weight loss, for example.
Although the cause of sarcoidosis is still not very well established, it is believed that it can be caused by the body's response to one or more invading agents, or even due to the body's reaction against itself, and is therefore considered an auto-disease -immune.
Sarcoidosis has no cure, however, it is of great importance to perform the treatment so that possible complications, such as respiratory and renal insufficiency, blindness and paraplegia, for example, are avoided.
Symptoms of sarcoidosis
According to the site where there is increased evidence of inflammation, sarcoidosis can be classified according to symptoms mainly in:
1. Pulmonary sarcoidosis
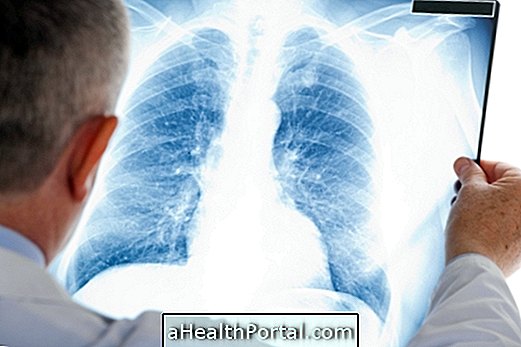
Lung involvement occurs in more than 90% of people diagnosed with sarcoidosis, and the inflammatory process can be seen through chest radiography. The main symptoms related to pulmonary sarcoidosis are dry and persistent cough due to obstructions in the airways, difficulty breathing and chest pain.
In addition, depending on the stage of inflammation, the person may present fibrosis of the lung tissue, requiring transplantation, in addition to pulmonary arterial hypertension.
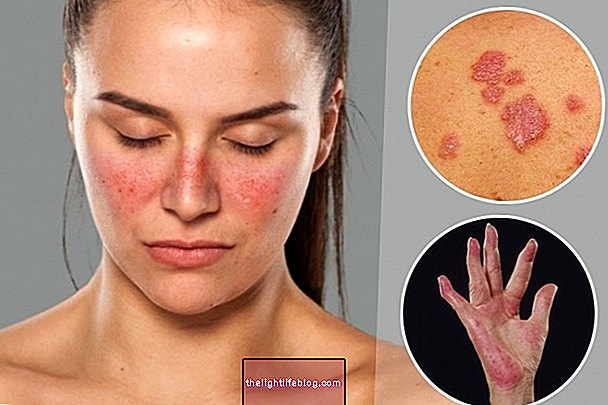
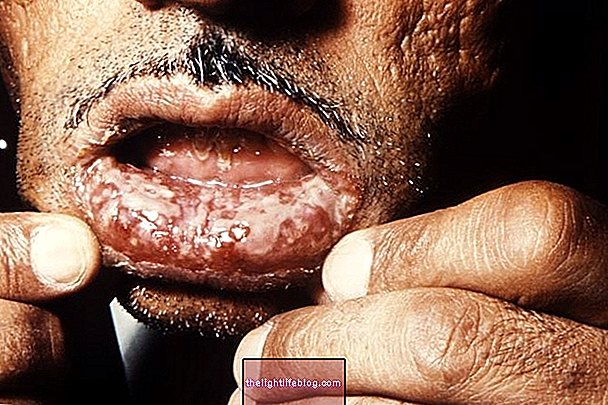
2. Sarcoidosis of the skin
In which there is the appearance of inflammatory lesions in the skin, being present in more than 30% of people diagnosed with sarcoidosis. The main symptoms of this type of saicoidosis are the formation of keloids, the appearance of red spots on the skin and changes in color, as well as the growth of balls under the skin, especially in areas close to scars.
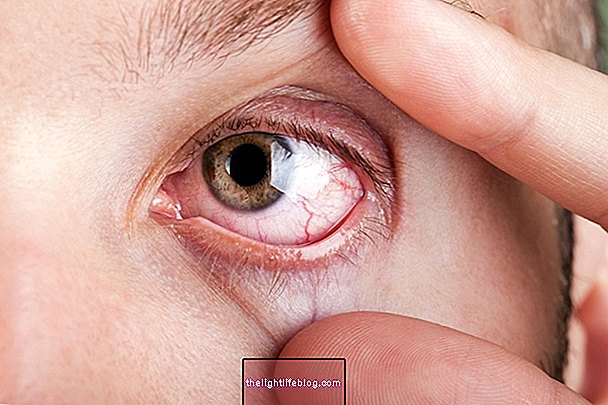
3. Ocular sarcoidosis
In the case of eye involvement, the most characteristic symptoms are blurred vision, pain in the eyes, redness, dry eyes and hypersensitivity to light. The frequency of clinical manifestations of sarcoidosis related to the eyes varies according to the population, being more frequent in Japanese.
It is important that eye symptoms are treated as otherwise it may result in blindness.
4. Cardiac sarcoidosis
Cardiac involvement in sarcoidosis is more frequent in the Japanese population and has as main symptoms heart failure and changes in heart rate.
How is the diagnosis made?
The initial diagnosis of sarcoidosis is made by the physician through the observation of symptoms and tests to indicate if there was compromised organs. Thus, the doctor may indicate, mainly, the chest radiography, since the lung is the organ most affected in this disease.
The diagnosis of this disease, however, is difficult, since the cause is still not very well established. Therefore, additional laboratory tests are usually required, as well as the biopsy of the granulomatous lesion or the affected organ and other imaging tests, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
How to treat
Sarcoidosis has no cure, however, the treatment aims to alleviate the symptoms and prevent the progression of the disease. Thus, your doctor may recommend the use of corticosteroid-based glucocorticoid drugs such as betamethasone or dexamethasone, or immunosuppressive drugs, such as azathioprine, for example.
In the case of organ involvement, it is important that the physician assess the extent of the impairment, as well as whether there is still any function, and organ transplantation may be required depending on the case.
It is also recommended that the person diagnosed with sarcoidosis be monitored periodically by the doctor, even if he does not present symptoms, so that the evolution of the disease and response to treatment can be verified.