Streptococcus corresponds to a genus of bacteria characterized by being rounded in shape and being arranged in chains, besides having violet or dark blue coloration when viewed through the microscope, and are therefore called gram-positive bacteria.
Much of the Streptococcus species can be found in the body, not causing any kind of disease. However, due to some situation, there may be an imbalance between the species of microorganisms that constitute the body and, consequently, the proliferation of this type of bacteria, which can cause serious diseases, if not treated.
Main species
Bacteria of the genus Streptococcus are small and immobile, since it does not have the structure responsible for locomotion, which are the flagella. In addition, most species are facultative anaerobes, that is, they are able to grow in environments with or without oxygen, and have an optimal temperature of growth around 37ºC. The main species of bacteria belonging to this genus are:
1. Streptococcus pyogenes
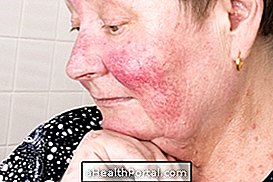
Streptococcus pyogenes, or S. pyogenes or Streptococcus group A, is the most pathogenic type for humans, although man is its natural reservoir. This bacterium is mainly present in the mouth and throat, and can be present in the skin and respiratory tract, so it can be easily transmitted from person to person by sharing cutlery, kisses or secretions such as sneezing and coughing, for example or through contact with wound secretions of infected persons.
The main way of entering S. pyogenes in the body is through the respiratory system, which may be the first site of infection or facilitate the occurrence of infections in other parts of the body, but not all people infected with this bacteria develop symptoms.
One of the main diseases caused by S. pyogenes is pharyngitis, which is characterized by sore throat, fever, malaise and headache. In addition to pharyngitis, S. pyogenes can cause scarlet fever, skin infections such as impetigo and erysipelas, as well as tissue necrosis and rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune disease characterized by the attack of the body itself to the immune system and that can be favored by the presence of the bacterium, having joint pain and heart involvement, for example. Learn how to identify and treat rheumatic fever.
Symptoms of S. pyogenes infection vary depending on the disease, however the most common symptom is persistent sore throat which occurs more than 2 times per year. The identification of the infection is done through laboratory tests, especially the antistreptolysin O, or ASLO, which allows to identify antibodies produced against this bacterium. Here's how to understand the ASLO exam.
Treatment for S. pyogenes infection depends on the disease the bacteria causes, and is mainly done with the use of antibiotics such as Penicillin and Erythromycin. It is important that the treatment is performed according to the doctor's advice, as it is common for this bacterium to acquire mechanisms of resistance, which can make the treatment complicated and result in serious health complications.
2. Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus agalactiae, or S. agalactiae or Streptococcus group B, are bacteria that can be found more easily in the lower intestinal tract and female urinary system and can cause serious infections in newborns.
Although it may be present naturally in the vagina of women, S. agalactiae may pose a risk to the baby, and may cause sepsis, pneumonia, endocarditis and even meningitis. This is because the bacteria present in the vagina can contaminate the amniotic fluid and be aspirated by the baby, which can result in septicemia for both the mother and the baby, and can be transmitted to the baby at the time of delivery.
The presence of this bacterium usually does not cause symptoms, but can be identified in the woman a few weeks before delivery so that the need to perform prophylactic measures to avoid infection in the newborn is verified. Infection with S. agalactiae in the baby can be identified by some characteristics, such as changes in consciousness, cyanosis and apnea, for example, which may occur within a few hours after delivery or two days later. Understand how the test is performed to identify the presence of S. pyogenes in pregnancy.
During pregnancy, S. agalactiae infection can result in miscarriage, infection in the amniotic fluid, sepsis at delivery, pneumonia and meningitis, for example. In the case of meningitis, the diagnosis is made through the culture of the cerebrospinal fluid in order to verify the bacterial growth. In addition, specific tests may be done to complete the diagnosis of S. agalactiae infection. The treatment is usually done with the use of antibiotics, being the most commonly indicated by the doctor Penicillin, Cephalosporin, Erythromycin and Chloramphenicol.

3. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or S. pneumoniae or pneumococcus, can be found in the respiratory tract of adults and, less frequently in children, and is responsible for diseases such as otitis, sinusitis, meningitis and, mainly, pneumonia.
Pneumonia is the main disease caused by this microorganism and can be identified by respiratory symptoms such as difficulty breathing, breathing faster than normal and excessive tiredness, for example. Get to know other symptoms of pneumonia.
Treatment for S. pneumoniae infection is done with the use of antibiotics, which should be recommended by the physician, such as Penicillin, Chloramphenicol, Erythromycin, Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim and Tetracycline.
4. Streptococcus viridans
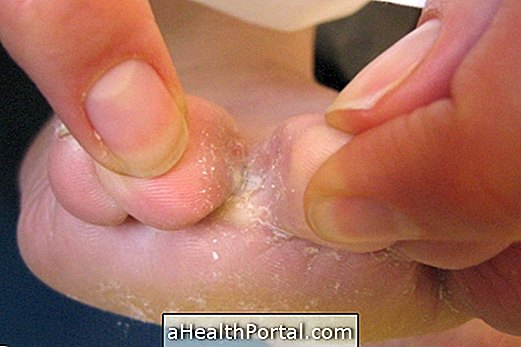
Streptococcus viridans, also known as S. viridans, constitutes mainly the oral and pharyngeal cavity and has a protective role, preventing the colonization of the region by pathogenic species of bacteria, such as S. pyogenes.
Streptococcus mitis, belonging to the S. viridans group, is present on the surface of the teeth and mucous membranes, and its presence can be identified through the visualization of dental plaques. These bacteria can enter the bloodstream during tooth brushing or tooth extraction, for example, especially when the gums are inflamed. However, in healthy people, these bacteria are easily eliminated in the bloodstream, but when the person has a predisposing condition, such as atherosclerosis, intravenous drug use or heart problems, for example, the bacteria can grow in a certain place in the body, resulting in in endocarditis.
Streptococcus mutans, which also belongs to the S. viridans group, is mainly present in the tooth enamel and its presence in the teeth is directly related to the amount of sugar consumed, being the main responsible for the occurrence of dental caries.
How to identify
The identification of infection by bacteria of the genus Streptococcus is done in the laboratory by means of specific examinations. The doctor will indicate, according to the symptoms presented by the person, the material that will be sent to the laboratory for analysis, such as blood, throat secretion, mouth or vaginal discharge, for example.
In the laboratory, specific tests are performed to indicate that the bacterium that causes the infection is Streptococcus, in addition to other tests that allow the identification of the bacterial species, which is important for the doctor to complete the diagnosis. In addition to the identification of the species, biochemical tests are carried out to verify the sensitivity profile of the bacteria, ie to determine the best antibiotics to combat this infection.