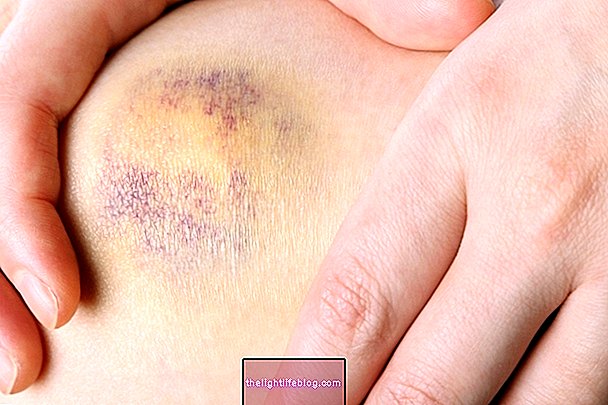
Edema, popularly known as swelling, occurs when there is a liquid build-up under the skin, which usually appears due to infections or excessive salt consumption, but can also occur in cases of inflammation, intoxication and hypoxia, which is when oxygen is lacking in a given part of the body, in addition to kidney, heart or lymphatic system disease.
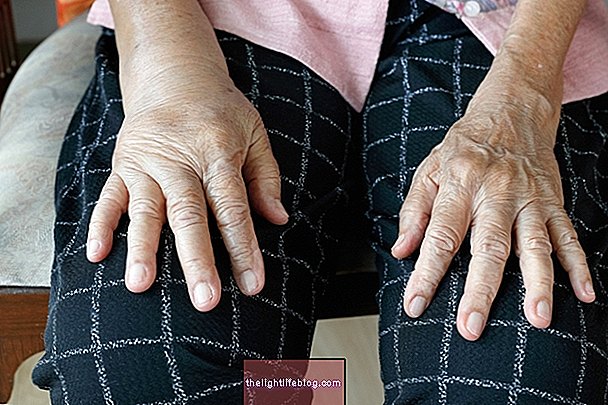
In this case, it is common for edema to appear on the hands, arms, legs, feet and face, causing the skin to be marked with a slight depression whenever pressure is applied to the affected area with a finger.Depending on the cause, the appearance of edema can happen suddenly, or gradually over the course of the day.
The treatment of edema must be individualized and focused on eliminating the cause, but generally the general practitioner indicates rest, elevation of the affected limb above the level of the heart and reduction in the amount of salt consumed daily, in addition to prescribing diuretic remedies, which help in release of excess liquid in the body through urine.

Main types of edema
Edema is classified into three types and aims to better clarify the cause and to know exactly what is the composition of the fluid that escaped under the skin.
The main types of edema are:
1. Common edema
Common edema is composed of water and proteins and is usually related to less serious situations, such as insect bites, falls or allergies to pollen, perfumes, makeup and dust, for example.
However, when it is generalized, that is, when it is present in various parts of the body, it can be a more serious situation, which needs medical attention at the health center or hospital. This condition can also be known as anasarca, which is more common in health problems such as liver cirrhosis, heart failure or nephrotic syndrome. Better understand what anasarca is and how the treatment is done.
2. Lymphedema
Usually lymphedema is composed of water, proteins and lipids, and it happens when the fluid that is part of the lymphatic circulation escapes to the skin and organs. This is more common in cases of cancer, elephantiasis and obstructed lymph nodes. See how lymphedema can be treated.
3. Myxedema
The main difference from myxedema is the high presence of lipids in its composition, which makes the swelling more firm than other types of edema, also with water and proteins. Myxedema most often affects the face, leaving the eyes swollen, but it can also be generalized.
This type of edema happens mainly when there is hypothyroidism or when hormonal treatment has been done.
Main symptoms
The main symptom of edema is the swelling of the affected region, but if the swelling is very large, it is possible to notice other symptoms, such as the more shiny and stretched skin. If the edema is in the feet or legs, when walking, the person may feel a slight burning and tingling.
If the edema does not disappear after a few hours, or if you have mild or moderate pain, and the skin becomes sensitive, it is recommended to seek an emergency room to assess the condition and check, using tests such as blood count, echocardiogram, X-ray and urine 24 hours, if it is not something more serious and that requires specific treatment.

Possible causes
The main diseases responsible for causing edema, can arise due to 4 types of changes in the body, such as:
1. Increased capillary pressure
The increase in capillary pressure is usually caused by the obstruction of veins, which can happen by the accumulation of fat, thrombi or by external compression, due to very tight clothes, for example. When this happens, the pressure that liquids make in blood vessels is greater than normal, so the liquids end up escaping from the vessels and accumulating in the tissues of the body.
Usually the causes related to this issue are heart, renal or venous failure, and in some cases, the diet high in sodium / salt. When these causes are not treated properly, they can lead to the appearance of pulmonary edema, in which fluids accumulate in the lung. Better understand what lung edema is and how to treat it.
2. Reduction of plasma proteins
When the levels of plasma proteins in the body are reduced, the reabsorption of fluids in the deeper layers of the skin does not happen, and this ends up leading to the accumulation of fluids under the skin, thus generating edema. As a consequence, this liquid, which is now in excess in the tissues, ceases to be in the circulation, which decreases the production of urine by the kidneys, resulting in more fluid inside the body, thus further increasing the edema.
Usually this type of edema appears in people who have nephrotic syndrome, liver disease, protein malnutrition, or who have suffered severe burns.
3. Increased capillary permeability
In this case there is a greater permeability of the blood vessels, usually caused by some inflammation, and, therefore, the liquids end up escaping from the vessels and accumulating in the tissues of the body.
Some conditions that can cause increased capillary pressure and edema are allergies, burns, vitamin C deficiency, infections, toxins or the use of vasodilators.
4. Blockage of lymphatic return
The edema caused by the blockage of the lymphatic return, also called lymphedema happens when there is an obstruction of the lymphatic vessels. This is common for hypothyroidism, cancer of the lymph nodes, or after lymphadenectomy.
The main characteristic of this edema, is that the swelling seems to be firmer to the touch and the skin can look like an orange peel. Learn how lymphedema can be treated.
How the treatment is done
The treatment for eliminating the edema must be according to the condition that caused it. In the mildest cases, rest, reduced salt intake in the diet and massage in the affected region are indicated, to help drain excess fluid, until the edema disappears.
In the most severe cases, where health conditions such as liver, kidney and other organs are present, it is necessary to treat the specific disease that caused the edema, in addition to the use of medications such as furosemide, bumetanide or spironolactone. See what other remedies can be used to deflate.
Care that prevents edema
Healthy changes in the daily routine that are maintained over time can help prevent and reduce the intensity and appearance of new edema, such as:
- Reduce the consumption of sodium and salt in the diet;
- Maintain the ideal weight for height, age and sex;
- Practice physical exercises regularly;
- Elevate your legs when lying down or sitting above your heart level.
These actions can be done by all people who do not have any chronic disease, however, for those who have a health problem, these practices must be indicated by a doctor responsible for treatment before they are started.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- MED J ARMED FORCES INDIA. Cerebral Edema and its Management. 2003. Available at:. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- J CLIN AESTHET DERMATOL. Management of Edema. 2017. Available at:. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- AMERICAN ACADEMY OF OPHTHALMOLOGY. What Is Macular Edema?. Available in: . Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- INFORMEDHEALTH. Causes and signs of edema. 2020.. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- BRAZILIAN ARCHIVES OF CARDIOLOGY. Generalized edema and hyperdynamic circulation - A possible case of beriberi. 2004. Available at:. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- PPAR RES. Renal and Vascular Mechanisms of Thiazolidinedione-Induced Fluid Retention. 2008. Available at:. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- //WWW.SCIELO.BR/SCIELO.PHP?PID=S1677-54492013005013055&SCRIPT=SCI_ARTTEXT&TLNG=PT. Investigation of postural edema of lower limbs in traffic agents. 2013. Available at:. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL THERAPY. Comparison between inferential measures of lower limb edema using the Leg-O-Meter and the water displacer. 2006. Available at:. Accessed on 07 Oct 2020
- Guyton & Hall. Treatise on medical physiology. 13th. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2017. 314-319.
- FILHO, Geraldo. Bogliolo General Pathology. 6th. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan LTDA, 2018. 166-169.







-o-que--como-identificar-e-o-que-fazer.jpg)