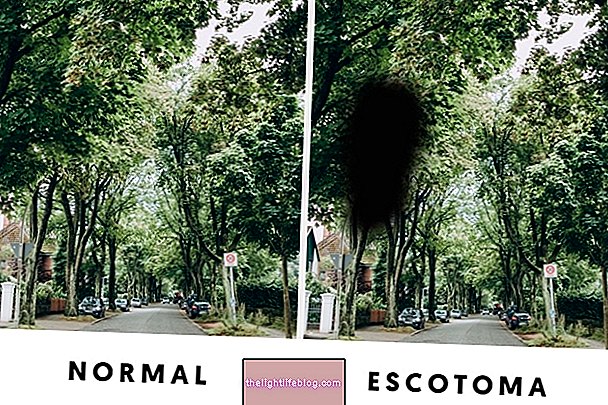
Nocturnal blindness, scientifically known as nicotopia, is the difficulty in seeing in dimly lit environments, such as at night, when it is darker. However, people with this change may have a completely normal vision during the day.
However, night blindness is not a disease, but a symptom or complication of another problem, such as xerophthalmia, cataracts, glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy. In this way, it is always important to consult an ophthalmologist to evaluate the presence of another eye disease and initiate appropriate treatment.
Thus, night blindness has healing, depending on its cause, especially when the treatment is started quickly and for the correct cause.
Symptoms and main causes
The main symptom of night blindness is the difficulty in seeing in dark environments, especially when moving from a very bright environment to a darker one, such as when entering the house or during sunset, for example. In this way, people with untreated night blindness should avoid driving at the end of the day or at night to ensure their safety.
This difficulty in seeing occurs when levels of a retinal pigment receptor, known as rhodopsin, are decreased, affecting the ability of the eye to process objects in low light.
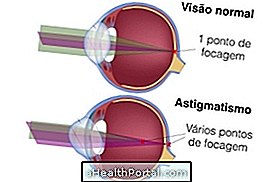
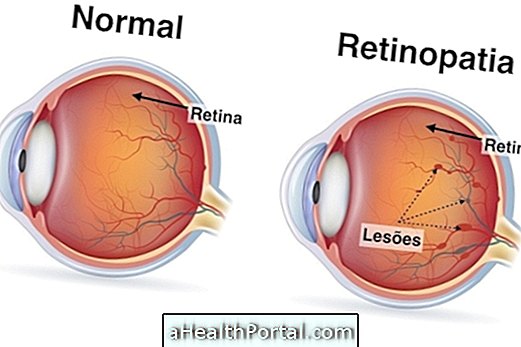
These receptors are usually affected by a lack of vitamin A, which causes xerophthalmia, but may also be altered in cases of other eye diseases such as glaucoma, retinopathy, myopia or retinitis pigmentosa, for example.
Learn more about how to identify and treat xerophthalmia.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for night blindness depends on the cause that is causing changes in the retinal receptors. Therefore, some of the most commonly used techniques include:
- Glasses and contact lenses : are used especially in cases of myopia to improve vision;
- Eye drops : they allow to control the pressure in the eye in cases of glaucoma, improving the symptoms;
- Vitamin A Supplements : are recommended in cases of xerlakia due to vitamin A deficiency;
- Surgery : widely used to treat cataracts in the elderly and improve vision.
In addition, if any other disease of the retina is identified, the doctor may ask for more tests such as optical tomography or ultrasound to confirm the treatment and may be more time consuming.