Luteinizing hormone, also called LH, is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland and, in women, is responsible for follicle maturation, ovulation, and progesterone production, and plays a key role in women's reproductive capacity. In men, LH is also directly related to fertility, acting directly on the testes and influencing the production of spermatozoa.
In the menstrual cycle, LH is found in higher concentrations during the ovulatory phase, but it is present throughout the woman's life, having different concentrations according to the phase of the menstrual cycle.
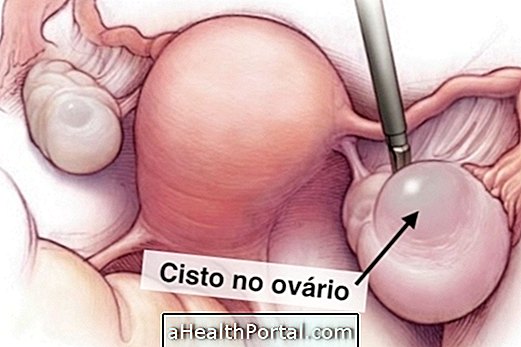
In addition to having an important role in verifying the reproductive capacity of men and women, the concentration of LH in the blood helps in the diagnosis of tumors in the pituitary gland and alterations in the ovaries, such as the presence of cysts, for example. This test is more often requested by the gynecologist to check the woman's health, and is usually requested along with the dosage of FSH and Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone, GnRH.
What is it for
The dosage of luteinizing hormone in the blood is usually requested to check the reproductive capacity of the person and to assist in the diagnosis of some changes related to the pituitary, hypothalamus or gonads. Thus, according to the amount of LH in the blood, it is possible to:
- Diagnosing infertility;
- To evaluate the capacity of human sperm production;
- Check if the woman has entered the menopause;
- To evaluate the causes of absence of menstruation;
- Check for adequate egg production for women;
- Assist in the diagnosis of pituitary tumor, for example.
In men, LH production is regulated by the pituitary gland and acts directly on the testes, regulating sperm production and hormone production, especially testosterone. In women, the production of LH by the pituitary stimulates the production of progesterone, mainly, and of estrogen, being fundamental for the pregnancy.
To assess the reproductive capacity of both men and women, the doctor may also be asked to also dose FSH, which is a hormone that is also present in a woman's menstrual cycle and influences sperm production. Understand what the purpose of FSH is and how to understand it.
Reference value
The reference values of luteinizing hormone vary according to the age, gender and phase of the menstrual cycle, in the case of women, the values being:
Children: less than 0.15 U / L;
Men: between 0.6 and 12.1 U / L;
Women:
- Follicular phase: between 1.8 and 11.8 U / L;
- Ovulatory peak: between 7.6 and 89.1 U / L;
- Luteal phase: between 0.6 and 14.0 U / L;
- Menopause: between 5.2 and 62.9 U / L.
The analysis of the results of the exams should be done by the doctor, since it is necessary to jointly analyze all the exams as well as the comparison with the examinations previously performed.

Low luteinizing hormone
When the LH values are below the reference value, it may be indicative of:
- Alteration in the pituitary, resulting in decreased FSH and LH production;
- Deficiency of gonadotropin production (GnRH), which is a hormone produced and released by the hypothalamus and whose function is to stimulate the pituitary to produce LH and FSH;
- Kallmann syndrome, which is a genetic and hereditary disease characterized by the absence of GnRH production, which leads to hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism;
- Hyperprolactinemia, which is increased production of the hormone prolactin.
The decrease in LH can lead to a decrease in the production of spermatozoa by man and in the absence of menstruation in women, a situation known as amenorrhea, and it is important to consult the doctor to indicate the best treatment, which is usually done with the use of hormonal supplementation .
High LH
The increase in LH concentration may be indicative of:
- Tumor in the pituitary gland, with increased secretion of GnRH and, consequently, of LH;
- Early puberty;
- Testicular insufficiency;
- Early menopause;
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
In addition, the hormone LH may be increased in pregnancy, because the hormone hCG can mimic LH and may appear high in the exams.