The diagnosis of meningitis is made through the clinical observation of the symptoms of the disease and confirmed by an examination called lumbar puncture, which consists of the removal of a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from the vertebral canal. This test can show if there is inflammation in the meninges and what the causative agent is essential for the diagnosis and to direct the treatment of the disease.
The tests and tests that can be requested by the doctor are:

1. Assessment of symptoms
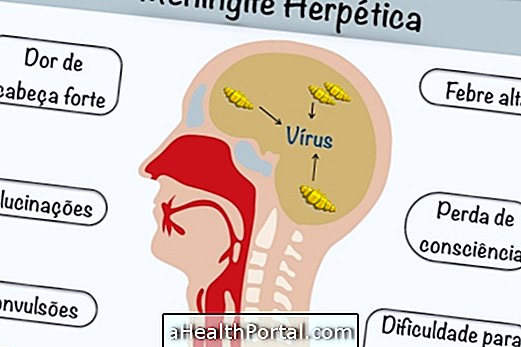
The initial diagnosis of meningitis is made through the evaluation of the symptoms by the physician, being observed if the person feels pain or difficulty in moving the neck, presents / displays fever high and dizziness, dizziness, difficulty of concentration, sensitivity to the light, lack of appetite, thirst and mental confusion, for example.
From the evaluation of the symptoms presented by the patient, the doctor may request further tests to complete the diagnosis. Get to know other symptoms of meningitis.
2. Culture of the CSF
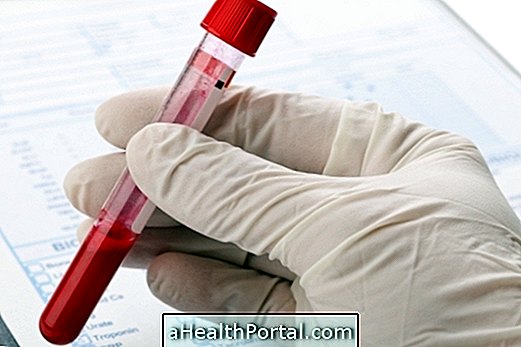
Culture of cerebrospinal fluid, also called cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), is one of the main laboratory tests required for the diagnosis of meningitis. This examination consists of the removal of a sample of CSF, which is a liquid found around the central nervous system, by means of a lumbar puncture, which is sent to the laboratory for analysis and research of microorganisms.
This test is uncomfortable, but rapid, and usually causes headache and dizziness after the procedure, but in some cases may relieve symptoms of meningitis by lowering cranial pressure.
The appearance of this liquid may already indicate if the person has bacterial meningitis because in this case the fluid may become cloudy and in the case of tuberculosis meningitis may become slightly cloudy, in other types the appearance can continue to be clean and transparent as water.
3. Blood and urine test
Urine and blood tests may also be ordered to help diagnose meningitis. Urine testing may indicate the presence of infections, due to the visualization of bacteria and numerous leukocytes in the urine, and thus, the urine culture may be indicated to identify the microorganism.
The blood test is also very requested to know the general condition of the person, which may indicate an increase in the number of leukocytes and neutrophils, in addition to being able to identify atypical lymphocytes in the case of the blood count, and increase in the concentration of CRP in the blood. indicative of infection.
Usually when there is a sign of bacterial infection, bacterioscopy can be recommended and, if the person is hospitalized, blood culture, which consists of the culture of the blood sample in the laboratory to verify the presence of infection in the blood. In the case of bacterioscopy, the sample collected from the patient is stained by Gram staining and then analyzed under a microscope to verify the characteristics of the bacteria and thus help in the diagnosis.
According to the results of the microbiological examinations, it is also possible to verify which antibiotic the microorganism is sensitive to, and is the most recommended for the treatment of meningitis. Learn how the meningitis treatment is done.
4. Image exams
Imaging tests, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, are only indicated when there is suspicion of brain damage or sequelae left by meningitis. There are suspicious signs of seizures, changes in the size of the pupils of the eyes, and tuberculous meningitis.
When diagnosing the disease the patient should remain hospitalized for a few days for the treatment to be initiated, based on antibiotics in case of bacterial meningitis or medicines to lower the fever and decrease the discomfort in case of viral meningitis.
5. Cup test
The cup test is a simple test that can be used to aid in the diagnosis of meningococcal meningitis, which is a type of bacterial meningitis characterized by the presence of red patches on the skin. The test consists of pressing a clear glass beaker on the arm and checking if the red dots remain and can be seen through the glass, which may characterize the disease.