Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, which is a membrane that surrounds the abdominal cavity and covers the organs of the abdomen, forming a kind of sac. This complication usually results from an infection, rupture or severe inflammation of one of the organs of the abdomen, such as by an appendicitis or pancreatitis, for example.
In this way, there are numerous factors that can lead to the development of peritonitis, such as gastrointestinal diseases, abdominal cavity lesions or medical procedures that lead to infection or irritation of the peritoneum, causing signs and symptoms such as abdominal pain and tenderness, fever, vomiting or imprisonment of belly, for example.
The treatment of peritonitis is indicated by the doctor and depends on its cause, but usually it is done with antibiotics and stabilization in a hospital environment, and surgery may also be indicated.
What are the signs and symptoms
The main symptom of peritonitis is abdominal pain and tenderness, which tends to worsen when performing movements or when pressing the region, for example. Other common signs and symptoms that may occur are abdominal distention, fever, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, decreased urine output, thirst and stopping stool and gas elimination.
To confirm the diagnosis of peritonitis, the doctor may make a clinical evaluation that shows typical signs of the disease, palpating the abdomen or asking the patient to stay in a certain position. In addition, blood tests that evaluate infections and inflammation, in addition to imaging tests such as radiography, ultrasound or tomography may be requested.
Possible causes
There are numerous causes of peritonitis. However, we mention here some of the most common:
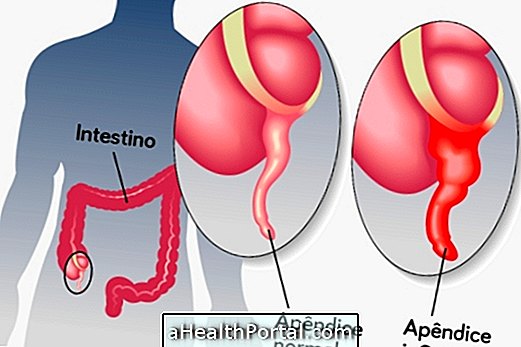
1. Appendicitis
Appendicitis is one of the main causes of peritonitis, because the inflammation that occurs in the appendix can extend through the abdominal cavity and reach the peritoneum, especially when it is not rapidly treated and presents complications such as rupture or abscess formation. Learn to recognize when abdominal pain can be appendicitis.
2. Gallbladder inflammation
Also called cholecystitis usually happens when a gallbladder calculus causes obstruction of the bile duct and then inflammation of this organ. This inflammation should be promptly treated by the physician, which includes performing surgery and using antibiotics.
If not treated properly, the inflammation of the gallbladder extends to other organs and to the peritoneum, causing peritonitis and other complications such as abscesses, fistulas, risk of generalized infection.
3. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, which generates symptoms that usually include abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea and vomiting. If not treated properly, the inflammation can become severe and lead to complications such as peritonitis, necrosis and abscess formation, putting the life of the affected person at risk. See more about pancreatitis.
4. Injuries to the abdominal cavity
Injury to the abdominal organs is due to ruptures, injuries due to trauma, complications after surgeries or even inflammation are important causes of peritonitis. This is because the lesions can release irritating contents to the abdominal cavity, as well as provoke contaminations by bacteria.
5. Medical procedures
Medical procedures such as peritoneal dialysis, gastrointestinal surgeries, colonoscopies, or endoscopies can cause peritonitis due to complications that may arise, whether due to perforations or contamination of surgical material.

6. Paralytic ileus
It is a condition in which the bowel stops functioning and its peristaltic movements cease to exist. This condition can arise after abdominal surgeries or situations such as inflammation, bruising, side effect of certain medications.
Symptoms caused by paralytic ileus include loss of appetite, constipation, vomiting or even intestinal obstruction which in more severe cases can lead to perforation of the intestine, leading to the spread of bacteria that cause peritonitis. Learn more about this disease.
7. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis consists of inflammation and infection of the diverticula, which are small folds or sacs that arise in the walls of the bowel, especially in the last portion of the colon, causing abdominal pain and tenderness especially in the lower part of the left side, in addition to diarrhea or constipation, nausea, vomiting, fever and chills.
Your treatment should be started quickly by the doctor, based on the use of antibiotics, analgesics, changes in diet and hydration, in order to avoid worsening inflammation and complications such as bleeding, fistula formation, abscesses, intestinal obstruction and peritonitis. Read more on everything about diverticulitis.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of peritonitis depends on its cause, but it is always advised to seek medical help as soon as possible so that treatment is started briefly to avoid complications.
Usually the treatment is done with the administration of antibiotics to treat the infection and prevent the spread of bacteria. At the same time, hospitalization is indicated where analgesics and anti-inflammatories are administered, fluids administered in the vein or oxygen.
In addition, if these measures are not sufficient to treat the problem, surgery may be necessary to resolve the cause of the inflammation, such as removal from the appendix, removal of an area of necrosis or drainage from an abscess, for example