Blount's disease, also called the tibia stick, is characterized by a change in the development of the cinnamon bone, the tibia, leading to progressive deformation of the legs.
This disease can be classified according to the age at which it is observed and the factors associated with its occurrence in:
- Infantile, when observed in both legs of children between 1 and 3 years, being more related to early gait;
- Late, when observed in one of the legs of children between 4 and 10 years or adolescents, being more related to being overweight;
The treatment of Blount's disease is done according to the age of the person and the degree of deformation of the leg, being recommended, in more severe cases, the accomplishment of surgery under general anesthesia followed by sessions of physiotherapy.
Main symptoms
Blount's disease is characterized by the deformation of one or both knees, leaving them arched. The main symptoms associated with this disease are:
- Difficulty walking;
- Difference in leg size;
- Pain, especially in adolescents.
Unlike the varus knee, Blount's disease is progressive, meaning the curvature of the legs can increase with the evolution of time and does not occur restructuring with growth, something that can happen in the varus knee. Understand what the varus knee is and how the treatment is done.
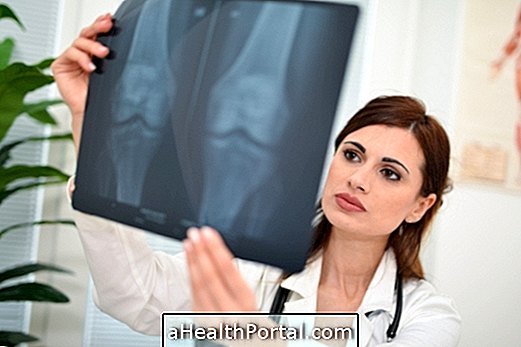
The diagnosis of Blount's disease is made by the orthopaedist through clinical and physical examinations. In addition, x-rays of the legs and knee are usually required to check the alignment between the tibia and the femur.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of Blount's disease is done according to the person's age and the evolution of the disease, and is recommended by the orthopedist. In children, treatment can be done through physical therapy and use of orthoses, which are equipment used to aid the movement of the knee and prevent further deformation.
However, in the case of adolescents or when the disease is already very advanced, surgery is indicated, which is done under general anesthesia and consists of cutting the end of the tibia, realigning it and leaving it in the correct place by means of plaques and screws. After surgery it is recommended to perform physiotherapy for knee rehabilitation.
If the disease is not treated promptly or in the right way, Blount's disease can lead to walking difficulty and degenerative arthritis of the knee, which is a condition characterized by stiffening of the knee joint that can lead to difficulty in feeling of weakness in the knee.
Possible causes
The occurrence of Blount's disease is usually related to genetic factors and, mainly, to the overweight of the children and to the fact that they started walking before the first year of life. It is unclear which genetic factors are associated with the occurrence of the disease, however it is proven that childhood obesity is associated with the disease due to increased pressure on the region of the bone responsible for growth.
Blount's disease can occur in both children and adolescents, being more frequent in children of African descent.