There are several options for the treatment of osteoarthritis, including analgesic remedies, anti-inflammatory drugs or supplements of glucosamine and chondroitin, for example, which are prescribed by the general practitioner, geriatrician or rheumatologist, depending on whether they cause symptoms, their intensity and the needs of each person.
In addition to using remedies to relieve symptoms, it is also essential to perform other alternatives such as physiotherapy and pilates, as a way to help strengthen muscles and protection of cartilages, as well as lose weight, practice physical activities, focus on adjustments in posture, and prefer a food with anti-inflammatory properties, rich in vegetables, seeds and fish.
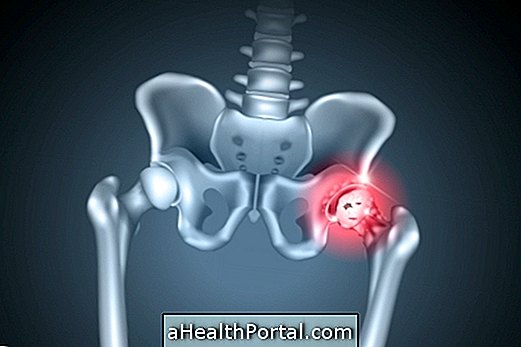
Arthrosis, or osteoarthritis, is a disease that degenerates the cartilages of the body, being common to affect places like knees, hands, spine and hip. Learn more about how to identify and what to do in case of this disease.

The main medications used to treat osteoarthritis are:
1. Analgesics
Paracetamol and Dipyrone are the main analgesics used to relieve osteoarthritis pain, and should be taken up to 4 times a day, or according to medical guidance, and are usually sufficient to allow daily activities.
However, these medications should be prescribed by the doctor and used according to the intensity of each person's symptoms.
Opioids, such as Codeine and Tramadol, are more potent analgesics, used in cases where the pain is very intense, or that does not improve with the usual analgesics. The stronger version of opioids, such as Morphine, Oxycodone and Methadone, for example, are also an option in those people who suffer from very intense and limiting pains.
2. Anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Diclofenac, Nimesulide, or Ketoprofen, for example, that can be taken as a tablet or an injection, are options to be used from time to time and to calm moments of crisis, only with doctor's prescription. This is because, if used too frequently, they cause several side effects, such as gastric ulcer and renal failure.
3. Nutritional Supplements
Supplements for cartilages like Glucosamine or Chondroitin are used to help regenerate, maintain elasticity and lubrication of joints, having good results in some people. The use of these substances can be done separately or together, as in Condroflex, and are found in pharmacies or homes of natural products.
4. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, may be options in some cases of constant pain associated with chronic inflammation, and should only be used under medical supervision.
These medications can also be injected directly into the joints by the doctor every 3 or 6 months, such as Dexamethasone and Betamethasone, helping to control inflammation and pain at the site.
Another injectable treatment option is hyaluronic acid, which helps reduce pain and improve joint mobility.
5. Ointments
Topical medications such as ointment or capsaicin anti-inflammatories are options for passing the inflamed site, helping to decrease pain and discomfort, and can be used 2 to 3 times a day for up to 20 days under medical guidance, which may prevent or lessen the need to use the tablets.

In the latter case, when the symptoms are very intense and do not improve with natural remedies and treatments, it is possible to perform surgery, which can remove inflamed parts or replace damaged cartilage. Learn more about the other treatment options for osteoarthritis.
Natural Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis
Home treatment for arthrosis is done as a way to help the doctor's treatment, never replacing it, to accelerate the recovery of pain and inflammation, or be an option for those people who have few symptoms or just want to prevent. It consists of:
- Perform physical activities, preferably swimming or water aerobics;
- Do physiotherapy and pilates exercises, at least twice a week, guided by the physiotherapist;
- Ergonomics, posture and use of mobility aids, such as restraints, ramps and handrails, at home and at work, by the physiotherapist and occupational therapist, are great for improving mobility and preventing symptoms;
- Massages with essential oils that help to deflate, such as ginger, lavender or basil may be useful for some people;
- Alternative techniques, such as acupuncture, can also be options to help treat some people by helping to control pain and discomfort.
There are also foods with anti-inflammatory properties, rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, calcium and protein, which can be adopted in the daily diet to help fight inflammation with fish, seeds, citrus fruits, red fruits, coconut oil and olive oil, for example. In addition, some teas can be prepared with plants that have anti-inflammatory properties, such as rosemary and sucupira, as a way to complement the treatment as directed by the doctor.
See more tips in the following video: