Heart pain is almost always associated with heart attack. This pain is felt as a tightness, pressure or under-the-chest weight lasting for more than 10 minutes, which can radiate to other regions of the body such as back, and is usually associated with tingling in the arms.
However, heart pain does not always mean heart attack, there are other conditions in which the main symptom is heart pain such as costochondritis, cardiac arrhythmia and even psychological disorders such as anxiety and panic syndrome. Learn what chest pain may be.
When heart pain is accompanied by some other symptom such as dizziness, cold sweat, difficulty breathing, tightness or burning in the chest, and severe chest pain, it is important to seek medical help so that diagnosis and treatment can be established as soon as possible. fast as possible.
1. Excess gases
Usually this is the most common reason for chest pain, not related to any heart condition. Gas buildup is very common in people who suffer from constipation, where excess gas pushes some of the abdominal organs and causes a sensation of pain in the chest.
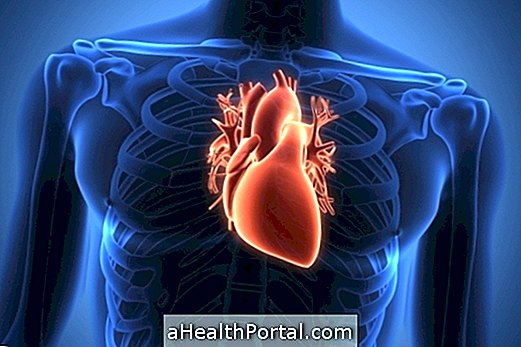
2. Heart Attack
Heart attack is always the first choice when it comes to heart pain, although it is rarely actually a heart attack only when you feel pain in the heart. It is more common in people with high blood pressure, older than 45 years, smokers or with high cholesterol.
The infarction is usually felt as a squeeze, but it can also be felt as pierced, stinging or burning that can radiate to the back, jaw and arms, causing tingling sensation. Learn more about identifying the symptoms of heart attack.
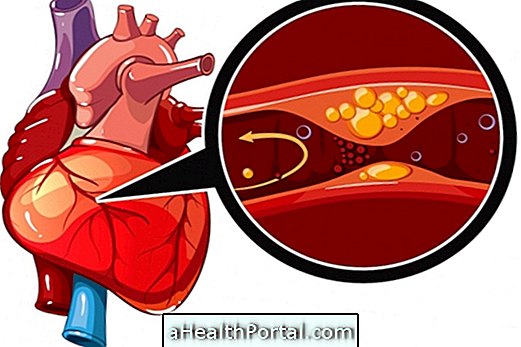
The infarction usually occurs when part of the tissue lining the heart dies, usually due to the decrease in the arrival of oxygenated blood to the heart because of the blockage of the arteries by fat or clot plates.
3. Costochondritis
Costochondritis usually occurs in women over the age of 35 and is characterized by inflammation of the cartilages that attach the ribs to the sternum bone, which is in the middle of the breast, due to poor posture, arthritis, excessive physical activity, or deep breathing. Depending on the intensity of the pain, the pain of the costochondritis can be confused with the pain felt in the infarction. Understand more about costochondritis.
4. Pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation in the pericardium, which is the lining of the heart. This inflammation is perceived through very strong pain that can be easily confused with the pain of the infarction. Pericarditis can be caused by infections or arise from rheumatic diseases such as lupus, for example. Learn more about pericarditis.
5. Cardiac ischemia
Cardiac ischemia is the decrease of the passage of blood through the arteries due to the presence of plaques that end up obstructing the vessel. This condition is noticed because of the strong pain or burning sensation in the chest, which can radiate to the nape of the neck, chin, shoulders or arms, as well as palpitation.
The main cause of cardiac ischemia is atherosclerosis, so the best way to avoid it is to have an active life, maintaining healthy habits and controlling food, not eating fatty foods or even with too much sugar. In addition, the physician may advise the use of medications that may facilitate the passage of blood by acting on the fat pad that blocks the vessel. Here's how to identify and treat heart ischemia.
6. Cardiac arrhythmia
Cardiac arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rhythm, ie, fast or slow heartbeat, and feeling of weakness, dizziness, discomfort, pallor, cold sweat, and heart pain. Learn other symptoms of arrhythmia.
Arrhythmia can occur in both healthy people and those who already have an established heart disease. Its main causes are high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, thyroid problem, intense physical exercise, heart failure, anemia and aging.
7. Panic Syndrome
Panic syndrome is a psychological disorder in which there are sudden seizures of fear that cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, cold sweat, tingling, loss of control over itself, ringing in the ear, palpitations and chest pain. in women in late adolescence and early adulthood.
The pain felt in the panic syndrome is several times confused with the pain of the infarction, however there are some characteristics that differentiate them. The pain in panic syndrome is acute and concentrated in the chest, chest and neck, while the pain of the infarction is stronger, it can be radiated to other regions of the body and lasts for more than 10 minutes. Learn more about this syndrome.
8. Anxiety
Anxiety can leave the person unproductive, that is, unable to perform simple tasks of everyday life. In anxiety attacks there is an increase in the tension in the ribs muscle and an increase in the heart rate, which causes a sensation of tightness and pain in the heart.
In addition to chest pain, other symptoms of anxiety include rapid breathing, rapid heartbeat, nausea, change in bowel function and a lot of sweating. Find out if you have anxiety.

What to do when you feel pain in the heart
If the heart lasts for more than 10 minutes or comes with other symptoms, it is important to get help from the cardiologist so that appropriate treatment can be started. Other symptoms that may accompany the pain are:
- Tingling;
- Dizziness;
- Cold sweat;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Severe headache;
- Nausea;
- Squeezing or burning sensation;
- Tachycardia;
- Difficulty in swallowing.
If preexisting heart disease, such as high blood pressure, is followed, medical advice should be followed so that these symptoms do not recur and the condition does not worsen. Also, if the pain is persistent and does not relieve after 10 to 20 minutes, it is strongly recommended to go to the hospital or call the family doctor.