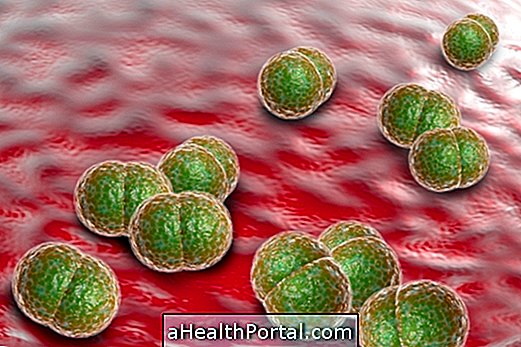
Pneumococcal meningitis is a type of severe meningitis that is caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is the same one that can cause the development of pneumonia.
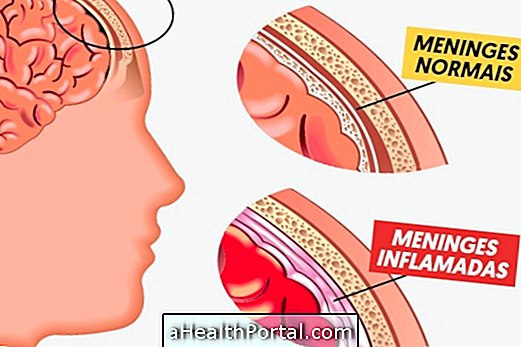
Usually, this type of bacteria is present in the nose or throat, but remains asleep, not causing any kind of symptom. However, some people are more sensitive to the bacteria and in this case it becomes active and can be transported through the blood to the brain where it causes inflammation of the membranes and causes symptoms such as:
- Fever above 38º C;
- Constant vomiting and nausea;
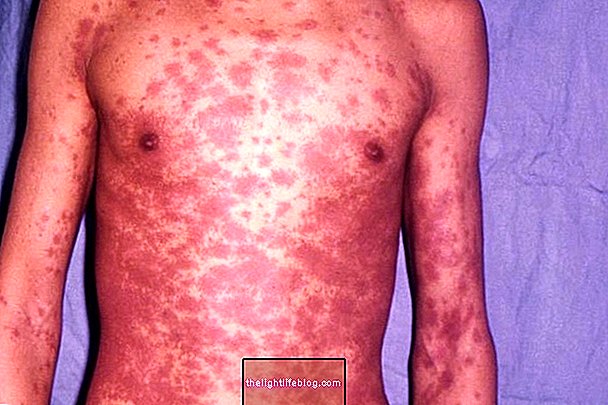
- Redness throughout the body;
- Difficulty in moving the neck;
- Hypersensitivity to light;
- Confusion and delusions;
- Convulsions.
In addition, when this type of meningitis occurs in babies, it can also cause other signs such as deep-knee, refusal to eat, excessive irritability or very stiff or completely soft legs and arms, such as a cloth doll.
Check how to identify cases of meningitis in infants or children.
What to do in case of suspicion
If these symptoms appear, it is recommended to go to the emergency room to confirm the diagnosis and start the appropriate treatment.
The diagnosis of pneumococcal meningitis is usually made by the physician through the observation of the symptoms, however, it is necessary to make an examination of the spinal fluid, which is the substance inside the spine. In this examination, known as a lumbar puncture, the doctor inserts a needle into one of the spine joints and withdraws some liquid to be evaluated and laboratory and confirm the presence of the bacterium.
How is the treatment done?
Pneumococcal meningitis should be treated as soon as possible to avoid complications such as hearing loss or cerebral palsy, for example, and increase the chances of cure.
Usually the treatment lasts about 2 weeks and is done at the hospital with the injection of antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin or Levofloxacin, directly into the vein to help fight the bacteria that are in the body causing meningitis. In addition, it may also be necessary to take corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in the membranes of the brain and relieve pain.
In more severe cases, where meningitis is identified too late or the disease is developing too fast, it may be necessary to be admitted to an ICU for constant observation.

What sequelae may arise
This type of meningitis is one of the most aggressive forms of the disease and so even with the correct treatment there is some chance of having sequelae such as hearing loss, cerebral palsy, speech problems, epilepsy or loss of vision. Learn more about the possible complications of this disease.
In some cases, these complications of meningitis may take a few months to appear or develop completely, and it is therefore necessary to have medical follow-up after discharge, especially after 4 weeks, when a example.
How to protect yourself
The best way to avoid developing pneumococcal meningitis is through vaccination against meningitis, which is included in the vaccination schedule and must be done within the first year of the baby's life. Understand how the Brazilian vaccination schedule works.
This is because the disease can not be transmitted from an infected person to a healthy one, since the bacteria usually do not cause symptoms even when it is present in the body.