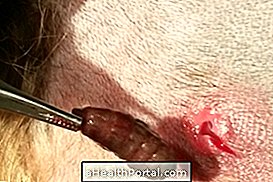
The enlarged lymph nodes, popularly known as navels, and scientifically as lymph node enlargement, most often indicate an infection or inflammation of the region in which they arise, although they may arise for a variety of reasons, from simple skin irritation, diseases of immunity, use of medicines or even cancer.
The lymph nodes, which are part of the lymphatic system, are an important part of the immune system, as they filter the blood and help eliminate harmful microorganisms. However, when they are enlarged, they are often visible or palpable in some specific regions, such as groin, armpit, and neck. Understand better the function of the lymph nodes and where they are.
Usually, the anus usually has benign and transient causes, and they are usually a few millimeters in diameter, disappearing in a period of about 3 to 30 days. However, if they grow more than 2.25 cm, last longer than 30 days or are accompanied by symptoms such as weight loss and constant fever, it is important to consult with a general practitioner or infectologist to investigate possible causes and recommend treatment .

Common Causes
Lymph nodes are small rounded structures, and when they are enlarged, they are usually noticed in nearby places where an infection or inflammation occurs, such as in the neck after a pharyngitis or in the groin after a genital infection, for example.
The causes are diverse, and it should be remembered that there is no rule. However, the most common causes include:
1. In the groin
The groin is the most common site where enlarged lymph nodes arise because the lymph nodes in this region may indicate the involvement of any part of the pelvis and lower limbs in situations such as:
- Sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis, soft cancers, donovanose, genital herpes;
- Genital infections, such as candidiasis or other vulvovaginitis, and penile infections caused by bacteria or parasites;
- Inflammation in the pelvis and lower abdominal region, such as urinary infections, cervicitis or prostatitis;
- Infections or inflammations in the legs, buttocks or feet caused by folliculitis, boils or even a simple ingrown nail;
- Other: some types of cancer, such as the cervix, ovary, genital region, anus or skin, for example, autoimmune diseases or systemic diseases.
In addition, since this set of lymph nodes is close to a region where there are often inflammations, minor cuts, or infections, it is common to notice aneurysms even without symptoms.
2. In the neck
The lymph nodes of the cervical region, but also those located under the mandible, behind the ears and the nape of the neck, are generally increased due to changes in the airways and the head region, such as:
- Respiratory tract infections, such as pharyngitis, colds, flu, mononucleosis, otitis and influenza;
- Conjunctivitis ;
- Skin infections such as folliculitis of the scalp, inflamed acne;
- Infections of the mouth and teeth, such as herpes, cavities, gingivitis and periodontitis;
- Less common infections such as tuberculous lymph node, toxoplasmosis, cat scratch disease or atypical mycobacterioses, even more rare may also cause this type of alteration;
- Other: some types of cancer, such as head and neck and lymphoma, for example, autoimmune diseases or systemic diseases;
In addition, systemic infectious diseases such as rubella, dengue or Zika virus may also manifest with enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. Learn more about diseases that cause neck disorders.

3. In the armpit
The axillary lymph nodes are responsible for draining the entire lymphatic circulation of the arm, chest wall and breast, so when they are enlarged, they may indicate:
- Skin infections, such as folliculitis or pyoderma;
- Infections of breast prostheses ;
- Other : breast cancer or autoimmune diseases.
The armpit region is also very susceptible to irritations from deodorants or depilation, or cuts due to the use of hair removal, which may also be causes of lymph node enlargement.
4. In other regions
Other regions may also have enlarged lymph nodes, however, they are less common. An example is the region above the clavicle, or supraclavicular, because it is not a common site for the appearance of enlarged ganglia, so the presence of this alteration may indicate a more serious disease, such as lung, esophagus, mediastinum, or intracancer -abdominal, for example;
In the anterior arm region, it may indicate infections of the forearm and hand, or diseases such as lymphoma, sarcoidosis, tularemia, secondary syphilis.
5. In various body locations
Some situations can cause enlargement of the lymph nodes in various parts of the body, both in the most exposed regions and in deeper regions, such as the abdomen or chest.
This is usually due to diseases that cause systemic or generalized involvement, such as HIV, tuberculosis, mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, leptospirosis, syphilis, lupus or lymphoma, for example, in addition to the use of certain medications, such as phenytoin.

When to see a doctor
The enlarged ganglion is generally characterized by having a fibrous and movable consistency, which measures a few millimeters and can be painful or not. However, there may be some changes that indicate worrying diseases, such as cancer, lymphoma or lymphoma, and some are:
- Measure more than 2, 5 cm;
- Have hard consistency, adhered to deep tissues and do not move;
- Persist for more than 30 days;
- Be accompanied by a fever that does not improve in 1 week, night sweats, weight loss or malaise;
- Have an epitrochlear, supraclavicular or scattered location throughout the body.
In this situation, it is necessary to seek care with a general practitioner or infectologist, so that the clinical evaluation, ultrasound examination or tomography, as well as blood tests that evaluate infections or inflammation by the body can be performed. When doubt persists, a ganglion biopsy may still be required, which will show whether it has benign or malignant features.