An aneurysm is the dilation of the wall of an artery that may end up rupturing and causing a hemorrhage or a stroke according to its location. The two most affected sites are the aortic artery, which carries the arterial blood out of the heart, and the cerebral arteries.
In either case, as it grows very slowly and causes no change in the body, the aneurysm rarely causes any kind of symptom.
However, when it grows too much, or very quickly, signs like:
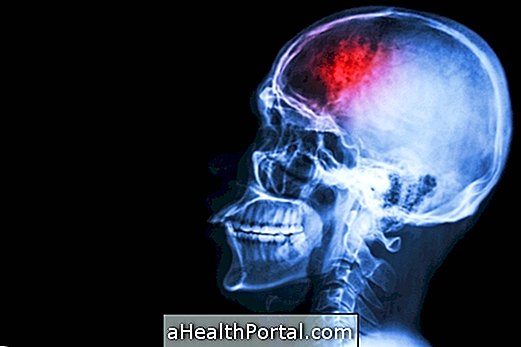
Brain aneurysm
- Persistent headache;
- Weakness and tingling in the head;
- Pupillary enlargement in only 1 of the eyes;
- Frequent seizures;
- Double or blurry vision.
Understand more about how to identify and treat a brain aneurysm.
Aortic aneurysm
- Pulsation in the abdominal region;
- Constant chest pain;
- Constant dry cough;
- Tiredness and shortness of breath;
- Difficulty swallowing.
See other signs of aortic aneurysm and how to do the treatment.
Thus, if more than one such symptom arises, it is advisable to consult a general practitioner to perform diagnostic tests, such as CT or MRI, and confirm the presence of the aneurysm.
What to do in case of suspicion
If there is more than one symptom, it is advisable to consult a neurologist in the case of a suspected cerebral aneurysm or a cardiologist in the case of a suspected aortic aneurysm for diagnostic tests such as computed tomography, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, for example.
Who is at increased risk of aneurysm
A specific cause for the development of an aneurysm is not yet known, but people who smoke, have high blood pressure, have atherosclerosis, or have had an infection in an artery have a higher risk of having the problem.
Also, having a history of aneurysm in the family, experiencing a serious accident or very strong knock on the body can also increase the chances of having an aneurysm.
How to identify emergency signals
In addition to the first symptoms, the aneurysm can cause abrupt changes that are usually related to its rupture. Symptoms of a rupturing brain aneurysm can be:
- Severe headache;
- Fainting;
- Constant vomiting and nausea;
- Hard neck;
- Difficulty walking or sudden dizziness;
- Convulsions.
These symptoms are a very serious situation that puts one's life at risk, so it is important to call for medical help immediately, calling 192, or taking the person to the emergency room.
Understand how the treatment of a brain aneurysm is done to prevent its rupture.