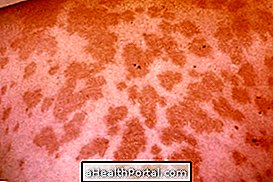
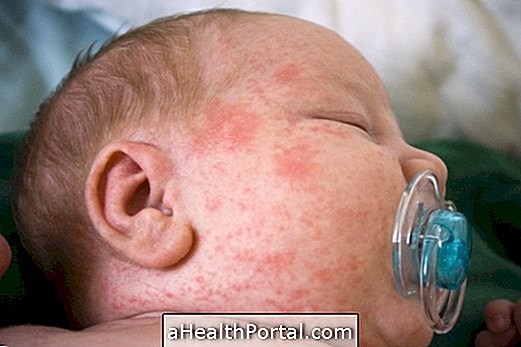
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin, also known as atopic eczema, which causes different skin lesions, such as plaques or small red lumps, which usually scratch and most often occur in infants or children up to 5 years of age. of appearing at any age.
This inflammation of the skin is allergic in origin and is not contagious, and the most affected sites vary according to age, being more common in the folds of the arms and knees, and may appear on the cheeks and near the ears of the babies, or in the neck, hands and feet of adults.
Although not curable, atopic dermatitis can be treated with anti-inflammatory medicines in ointment or tablets, and with skin hydration.
 Dermatitis in the baby
Dermatitis in the baby  Adult dermatitis
Adult dermatitis How to identify
Atopic dermatitis can appear in any baby or adult who suffers from some type of allergy and is very common in people who have allergic rhinitis or asthma and therefore is considered a form of allergy to the skin. This reaction can happen at any time but can also be triggered by allergy to a food, dust, fungi, heat, sweat or as a response to stress, anxiety and irritability.
In addition, atopic dermatitis has genetic and hereditary influences, as it is very often that the person with this disease has parents also allergic. The most common symptoms are:
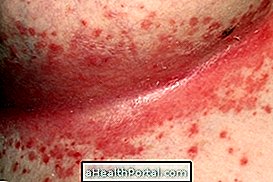
- Swelling of the skin;
- Redness;
- Itching;
- Desquamation of the skin;
- Formation of small balls.
These lesions can often appear in periods of outbreak and disappear when the allergic reaction improves. However, when the lesions are not treated or remain in the skin for a long time, they may become darker and appear as a crust, a situation called lichenification. Learn in more detail the symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
As the allergic reaction causes itching and wounds, there is a strong predisposition for infection of the lesions, which may become more swollen, sore and with purulent secretion.
How to treat
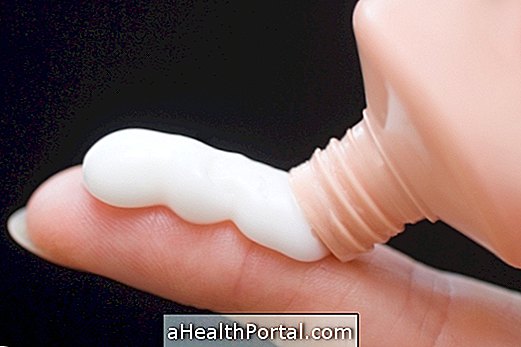
Treatment for atopic dermatitis can be done with the use of corticoid creams or ointments prescribed by the dermatologist, such as Dexchlorpheniramine or Dexamethasone, 2 times a day. Learn more about what remedies are used to treat atopic dermatitis.
It is still important to adopt some habits to reduce inflammation and treat seizures, such as:
- Use moisturizers, based on urea, avoiding products such as color and smell;
- Do not bathe with hot water;
- Avoid taking more than one bath per day;
- Avoid foods that are more likely to cause allergies, such as shrimp, peanuts or milk. Learn more in nutrition to improve dermatitis.
In addition, tablet medications, such as antiallergic or corticoids prescribed by the dermatologist, may be needed to reduce itching attacks and severe inflammation.