An injury to the knee ligaments is a potentially serious emergency situation which, if left untreated, can have unpleasant consequences.
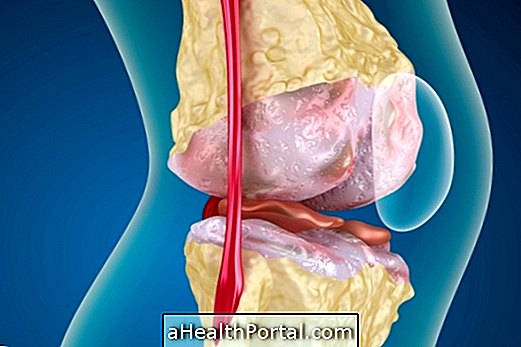
The knee ligaments serve to give stability to this joint, so when one of the ligaments is broken or compromised, the knee becomes unstable and causes a lot of pain.
Most of the time, an injury to the knee ligaments is caused by a great sudden effort. Treatment for such an injury is often surgical, followed by a few months of physiotherapy and rest, but initially it may be necessary to use a knee brace to prevent knee movements.

Physiotherapeutic treatment for the knee
The physiotherapeutic treatment for knee rehabilitation should be chosen by the physiotherapist himself who will treat the individual. Some techniques that he can use are:
- Laser: to decrease pain and facilitate healing;
- Ice: to decrease swelling and numb the place for deep transverse massage;
- Manual joint mobilization: to lubricate the joint, confer range of motion and release adhesions;
- Mobilization of the patella: to increase knee flexion;
- Knee traction: to increase interarticular space;
- Russian current: to improve anterior and posterior thigh muscle tone;
- Thera-band exercises: for overall strength gain with thigh and leg muscles;
- Proprioception exercises with eyes open and closed.
During physiotherapeutic treatment for recovery of knee ligaments, it is normal for some other situations, such as tendonitis, difficulty in bending and stretching the leg and muscle weakness, which should also be treated at the same time.
Medial or lateral collateral ligament
Treatment for repair of medial or lateral collateral ligaments can be performed with physical therapy and rarely require surgery. Physiotherapy should be started soon after diagnosis and may include the use of devices and exercises prescribed by the physiotherapist.
To speed recovery it may be necessary to use an ice pack exactly at the injury site for about 15 minutes twice a day, and use a knee brace to protect the knee from any complications.
In the clinic, the physiotherapist can use devices such as tension, ultrasound, laser, in addition to stretching exercises and muscle strengthening. Surgery may be indicated when the ligament was completely ruptured, evidencing a grade 3 lesion in athletes.
Learn more about Physiotherapy for Anterior Cruciate Ligament rupture.
Anterior or posterior cruciate ligament
Treatment for anterior or posterior cruciate ligament injuries may include physiotherapy sessions or, in some cases, ligament reconstruction surgery, which is indicated particularly when the knee is very unstable or the patient is an athlete.
Physiotherapy equipment may be helpful in facilitating healing and fighting pain but strengthening the thigh muscles and the back of the leg are very important to speed recovery.
Signs of better and worse
Signs of improvement include decreased pain, swelling, and the ability to walk and move without pain or limping, while the signs of worsening are just the opposite.
Complications of knee injuries
The main complication of knee ligament injuries is the increased risk of knee meniscus injury, constant pain and permanent knee instability, which can be avoided with the indicated treatment. Here's how to identify and treat a meniscal injury here.
See too:
- What to do when your knee is swollen
- 5 Tips to Relieve Knee Pain
Proprioception Exercises for Knee Recovery