Cytomegalovirus contracted in pregnancy should be treated as soon as possible to prevent contamination of the baby through the placenta or during delivery.
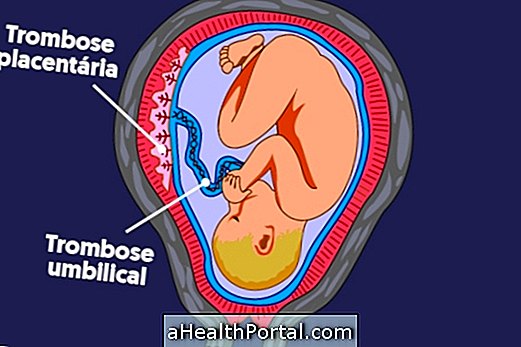
Generally, the pregnant woman comes in contact with the cytomegalovirus before pregnancy and, therefore, has antibodies capable of combating the infection and avoiding transmission. However, when the infection occurs shortly before or during pregnancy, there are chances of transmitting the virus to the baby, leading to premature delivery and even malformations in the fetus, such as microcephaly, deafness, mental retardation or epilepsy.
Cytomegalovirus in pregnancy has no cure, but it is usually possible to start antiviral treatment to prevent transmission to the baby.
How to treat cytomegalovirus in pregnancy
Treatment for cytomegalovirus in pregnancy can be done with ingestion of antiviral medicines such as acyclovir or injection of immunoglobulins prescribed by the obstetrician to prevent transmission to the baby.
During treatment for cytomegalovirus during pregnancy, the doctor should perform regular tests to monitor the development of the baby. Learn more about treatment of cytomegalovirus in pregnancy in: Treatment for cytomegalovirus in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of cytomegalovirus in pregnancy
The diagnosis of cytomegalovirus in pregnancy is made with the CMV blood test during pregnancy, the result being:
- Non-reactive or negative IgM and reactive or positive IgG : the woman has had contact with the virus for a longer time and the risk of transmission is minimal.
- IgM reagent or positive and IgG non-reactive or negative : acute infection by cytomegalovirus, is more worrisome, the doctor should guide.
- IgM and IgG reagents or positive : an avidity test must be performed. If the test is less than 30%, there is a higher risk of infection of the baby during pregnancy.
- Non-reactive or negative IgM and IgG : there has never been contact with the virus and therefore any contact should be avoided.
When there is suspicion of infection in the baby, a sample of amniotic fluid may be withdrawn to evaluate the presence of the virus. However, according to the Ministry of Health, the examination in the baby should only be done after 5 months of pregnancy and 5 weeks after the infection of the pregnant woman.
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus in pregnancy
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus in pregnancy may be swollen and painful armpits, muscle pain and fever above 38 ° C.
However, most pregnancies do not show any symptoms and the infection is only diagnosed on a routine blood test.
What to do to prevent cytomegalovirus in pregnancy
To avoid cytomegalovirus in pregnancy the pregnant woman should follow some recommendations, such as:
- Use a condom in intimate contact;
- Do not go to work, especially if working in public places;
- Wash your hands immediately after changing the diaper to a baby or whenever it comes in contact with the child's secretions, such as saliva, for example;
- Do not kiss very young children on the cheek or mouth;
- Do not use objects that are childlike, such as cups or cutlery.
Children are primarily responsible for the transmission of cytomegalovirus, so these recommendations should be followed by the pregnant woman throughout pregnancy, especially if working with children.