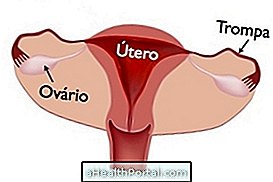
Inflammation in the fallopian tubes is called salpingitis and may make pregnancy difficult by preventing the mature egg from reaching the fallopian tubes, where fertilization normally occurs, which is the entry of the spermatozoid into the ovum, which gives rise to the embryo. In addition, salpingitis increases the chances of pregnancy in the fallopian tubes.
This inflammation can reach only one or both of the tubes, and can be acute, if diagnosed and treated soon, or chronic, when the inflammation lasts many years. Some of the symptoms of salpingitis are pain during intimate contact and foul-smelling vaginal discharge, and your treatment is done with the use of antibiotic and anti-inflammatory medications.
Symptoms of inflammation in the tubes
The symptoms of salpingitis vary according to the severity and duration of the problem, but usually arise after menstruation and can be:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge, with bad smell;
- Changes in the menstrual cycle;
- Pain during ovulation;
- Pain during intimate contact;
- Fever;
- Abdominal pain on both sides;
- Pain in the lower back;
- Pain when urinating;
- Nausea and vomiting.
Salpingitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection such as chlamydia or as a result of infections in the abdomen, vagina or uterus. However, procedures such as uterine biopsy, hysteroscopy, IUD placement, delivery or abortion may increase the risk of developing salpingitis.

Diagnosis of inflammation of the tubes
The diagnosis of salpingitis can be made based on the symptoms presented by the woman and blood and urine tests. In addition, complementary examinations such as salpinography and diagnostic laparoscopy may be used to confirm the presence of inflammation of the tubes.
Treatment for chronic inflammation in the fallopian tubes
Treatment of salpingitis includes the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatories, as well as pain-relieving medicines. If salpingitis is related to IUD use, treatment also involves withdrawal, but more severe cases may require treatment at the hospital or surgery to remove the fallopian tubes and uterus.
During treatment of the infection, the woman should stay at rest and drink plenty of water. In addition to the woman, your partner should also take antibiotics during the treatment of inflammation, to make sure that the infection is eliminated and there are no recurrences of the condition.
See too:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic inflammatory disease










-o-que--e-para-que-serve.jpg)




-causas-e-como-tratar.jpg)