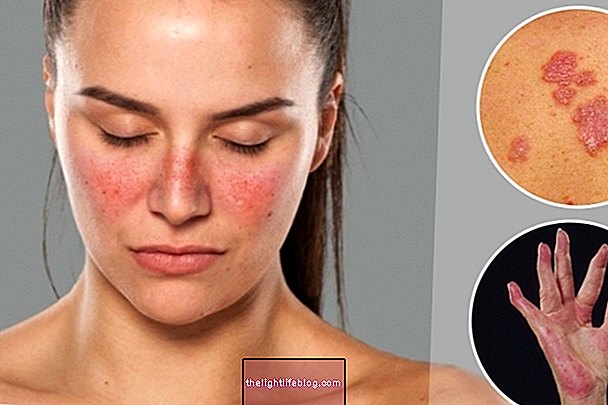
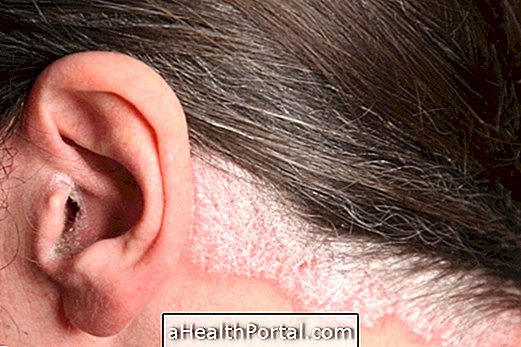
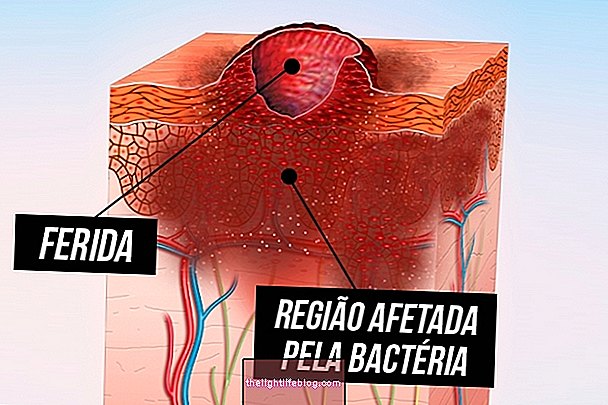
Infectious cellulitis is a disease that affects the deeper layers of the skin, caused by bacteria that penetrate the body through a wound, such as a cut, ringworm or insect sting, for example. It is characterized by redness, pain and swelling of the affected site and other symptoms such as fever and chills. Although infectious cellulitis is more common in the legs and feet, it can also occur on the face. Understand what infectious cellulitis is, possible causes and how to confirm the diagnosis.
Because it is caused by bacteria, the treatment of infectious cellulitis is done with the use of antibiotics that should be used according to the recommendation of the dermatologist. In addition, it is important to hydrate the skin to avoid cracking and treat the wounds properly, since they facilitate the entry of the bacteria into the skin. Here's how to do a wound dressing.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for infectious cellulitis or bacterial cellulitis is done with oral antibiotics, such as cefalexin and amoxicillin, resting and elevating the affected limb with cushions, to reduce the swelling and pain characteristic of this disease.
In addition, the doctor may also prescribe analgesic and antipyretic medicines, such as dipyrone and paracetamol, to reduce fever, which may occur in some cases.
It is very important for the patient to do the treatment correctly, taking the antibiotics prescribed by the dermatologist to the end, to prevent the bacteria from entering the bloodstream and causing a generalized infection of the organism, known as septicemia or septic shock. Understand septic shock, symptoms and how the treatment is done.
Usually, the treatment lasts for 14 days and depending on the severity of bacterial cellulitis, the patient's symptoms and the presence of other chronic diseases, such as diabetes, it may be necessary for the individual to be hospitalized to receive the antibiotic through the vein.
Side effects
The most common side effects of treatment for infectious cellulitis are mild digestive problems such as stomach pain, nausea or episodes of diarrhea due to the use of antibiotics.
Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement in infectious cellulitis include the decrease and disappearance of redness of the skin, pain and swelling.
Signs of worsening
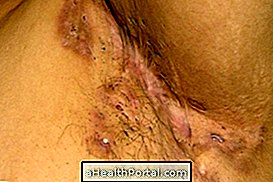
Signs of worsening infectious cellulitis arise when treatment is started late or incorrectly and in this case blisters may appear in the affected site, the skin begins to turn black and the individual has no sensitivity at the site. In addition, there may be septicemia followed by death.
Home Treatment for Infectious Cellulitis
A great home treatment for infectious cellulitis are chamomile compresses. To make this natural treatment for infectious cellulitis, simply make the chamomile tea, let it cool and then, with a clean glove, moisten a sterile compress on the cold tea and apply in the affected place for a few minutes.
It is important to use sterile compresses to avoid injury and clean gloves to avoid having infectious cellulitis in the hand if there is any injury. In addition, it is important to moisturize the skin to avoid cracking, pay attention to the signs of infection in small wounds, and take good care of the wounds on the skin, thus avoiding the penetration of the bacteria.