Bursitis in the hip, also known as trochanteric bursitis, consists of a painful inflammatory process of synovial bursae, which are small pockets of connective tissue filled with synovial fluid located around some joints that function as a surface that reduces friction between the bone and tendons and muscles.
This problem can be caused by diseases, muscle weakness or intense physical exercise that can cause overload in these structures. The treatment consists of the administration of anti-inflammatories, physical therapy and in more severe cases it may be necessary to resort to surgery.
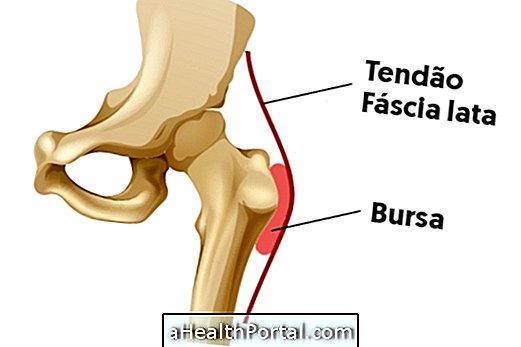
Possible causes
Bursitis in the hip can be caused by overloading of the tendons and bursae, which can be caused during intense physical activity or exercises in which repetitive movements are performed. This inflammation can also occur due to situations of muscle weakness, where even mild activities may be enough to cause injury.
There are diseases that are also a risk factor for developing this problem, such as lumbar spine disease, sacroiliac joint disease, rheumatoid arthritis, knee osteoarthritis, gout, diabetes, infection by a bacterium called Staphilococus aureus or scoliosis.
In addition, hip injuries, previous hip surgeries, ankle sprain, leg length discrepancy, shortening of the fascia lata, and having broad hips are also factors that can sometimes affect walking and overloading bursae and tendons. lead to a bursitis in the hip.
What are the signs and symptoms
The most common symptoms that can occur during a bursitis in the hip are:
- Pain in the side of the hip that may increase in intensity when standing for a long time or lying on its side;
- Pain to touch;
- Swelling;
- Pain radiating to the thigh.
If this disease is not treated, it can become chronic, becoming more and more difficult to treat and control the symptoms.
Which exercises are recommended
The recommended exercises for hip bursitis have the purpose of strengthening the muscles of the gluteal region, especially the affected muscles and also the muscles of the lower limb.
1. Make the bridge

Bridging the hip helps to work with muscles such as hip flexors, buttocks, hamstrings, and quadriceps, which are very important to support the hip joints and is therefore a good exercise to strengthen the hip.
To do this exercise, one should start by lying on his back with his feet flat on the floor and his legs bent and then lifting only the hips, so as to form a straight line between the shoulders and knees. Then you should slowly resume the previous position and do 5 sets of 20 repetitions.
In order to increase the difficulty and to obtain better results, 5 series with more repetitions can be made.
2. Raise the legs aside

This exercise helps strengthen and develop the iliotibial band, which is located on the outside of the thigh and also helps strengthen the glutes.
To do this exercise, one should lie down to the right side, stretching the right arm to assist in balance during exercise and lift the right leg up as much as possible and back down toward the other leg. The ideal is to perform 4 sets of 15 repetitions on each leg.
3. Circling with the legs

This exercise helps improve range of motion, flexibility, and strength in all muscles that make hip and leg rotation possible, such as hip flexors and buttocks.
To perform this exercise correctly, the person should start by lying on his back with his legs stretched out. Next, raise your right leg slightly and make small circles, keeping it always straight. There should be 3 sets of 5 rotations per leg.
4. Raise your standing legs

With a chair in front to support or with the help of someone, one should lift one of the legs bent while the other remains stretched and then repeat the movement with the other leg and go alternating the two, doing about 3 sets of 15 repetitions.
In order to get better results, these exercises should be performed about 4 to 5 times a week.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is made through physical evaluation, in which the doctor evaluates the sensitivity in the region, analyzes the symptoms described by the person and performs strength tests of the muscles related to that region. The evaluation can become painful because during the execution it occurs tensioning of the tendons and compression of the inflamed bursas.
The detection of inflammation can also be done through examinations such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. An X-ray can also be performed to exclude a possible suspicion of another type of injury, such as a fracture, for example, or to see if there is any factor related to hip bursitis.
ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging
What is the treatment
Bursitis on the hip is healing and treatment can be done with joint resting as long as possible, application of ice in the area and, if necessary, use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen to relieve pain and swelling or the natural painkillers referred to in the following video:

Physical therapy is a great treatment option because good results are usually obtained because it reduces the inflammation process, relieves pain and reduces overload on inflamed bursae.
In addition, in more severe cases, the doctor may also administer an injection with corticosteroids or an infiltration, which consists of a local injection of anesthetic medication. Although rare, it may be necessary to resort to surgery in which the inflamed bursa is removed and the tissues from the lateral region of the hip are also released and repair of injured tendons. See more about bursitis treatment.