Some women often experience pain in the ovary, but this is usually related to the menstrual cycle and therefore is not a cause for concern as it is triggered by the ovulation process.
However, ovarian pain may also be related to some disease such as endometriosis, cysts or pelvic inflammatory disease, especially when you are not menstruating. Therefore, it is important that the woman is attentive to all the signs and symptoms, if necessary consult the gynecologist.
1. Ovulation
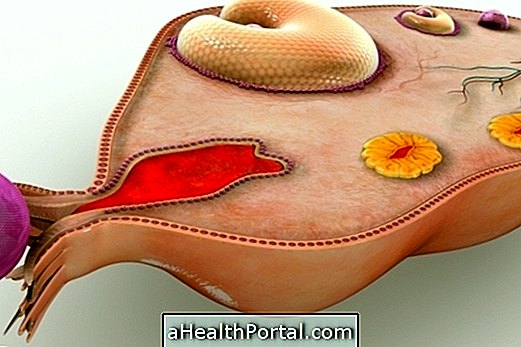
Some women may experience pain at the time of ovulation, which occurs around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle, when the ovum is released by the ovary into the fallopian tubes. This pain may be mild to severe and may take a few minutes or even hours and may be accompanied by slight bleeding and in some cases the woman may also feel sick.
If this pain is very intense, or if it lasts for several days, it can be a sign of diseases such as endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy or the presence of ovarian cysts.
- What to do: There is usually no need for treatment for pain caused by ovulation, however if the discomfort is too great you may need to take painkillers like paracetamol, or anti-inflammatories like ibuprofen or talk to your doctor to start taking a contraceptive.
2. Ovary cyst

The cyst in the ovary is a fluid-filled pouch that may form in or around the ovary, which may cause pain on the side of the cyst, pain during ovulation and during intimate contact, delayed menses, increased breast tenderness, vaginal bleeding, weight gain and difficulty getting pregnant. Learn about the major types of ovarian cyst and how to identify it.
- What to do: The cyst on the ovary usually shrinks in size without the need for treatment. However, if this does not happen, the cyst can be treated by taking the contraceptive pill or even resorting to surgery that involves removing it. If the cyst is very large, shows signs of cancer or in case of twisting of the ovary, it may be necessary to completely withdraw the ovary.
3. Twisting the ovary

The ovaries are trapped in the abdominal wall by a thin ligament, through which the blood vessels and nerves pass. Sometimes this ligament may end up bending or twisting, which causes intense, constant pain that does not improve.
Torsion of the ovary is more frequent when there is a cyst in the ovary, as the ovaries become larger and heavier than normal.
- What to do : Torsion of the ovary is an emergency situation, so if you experience a very intense and sudden pain it is important to go to the emergency room to identify and start the appropriate treatment.
4. Endometriosis

Endometriosis can be another cause of ovarian pain, which consists of the growth of endometrial tissue outside its normal location, such as outside the uterus, ovaries, bladder, appendix or even intestines.
Thus, endometriosis can cause symptoms such as severe pain in the belly that can radiate to the back, pain after intimate contact, painful urination and defecation, heavy bleeding during menstruation, difficulty becoming pregnant, diarrhea or constipation, tiredness, nausea and vomiting.
- What to do: There is still no cure for endometriosis, but treatment can help relieve the symptoms. To treat endometriosis can be used medicines like the contraceptive pill or IUD, which help reduce the growth of endometrial tissue, or anti-hormonal remedies such as Zoladex or Danazol, which reduce the production of estrogen by the ovaries, avoiding the menstrual cycle and thus preventing the development of endometriosis. In addition, surgery can be used to remove endometrial tissue outside the uterus, in order to reduce symptoms and enable pregnancy. Learn more about how surgery for endometriosis is done and what the risks are.
5. Pelvic inflammatory disease

Pelvic inflammatory disease consists of an infection that begins in the vagina or cervix and reaches the endometrium, fallopian tubes and ovaries, causing symptoms such as fever, belly pain, vaginal bleeding and discharge, and pain during intimate contact. See more about this disease.
What to do: The treatment involves the use of antibiotics for about 14 days, which should also be done by the partner and avoid intimate contact during treatment.