Diabetes increases the risk of genital infections such as candidiasis, ringworm and urinary tract infection in both men and women, especially when the amount of sugar in the blood remains uncontrolled for a long time. This risk increases because hyperglycemia weakens the immune system, making it harder to fight microorganisms that cause infections.
Therefore, keeping blood glucose properly controlled and preventing the complications of diabetes helps prevent this type of infection.
Most common infections in diabetics
The most common infections in diabetics are:
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is caused by the fungus Candida and is characterized by itching, redness and whitish plaques in the affected region. This disease usually develops in the genital region or in the mouth, but can also appear on the skin and nails.
The treatment for candidiasis is made with antifungal medicines, in the form of tablets or ointments that should be applied at the site of infection, according to medical advice. In addition, when the infection is recurrent, it is important that the partner of the affected person also do the treatment, to prevent further contamination. See the symptoms and how to treat all types of candidiasis.
Urinary infection
The urinary tract infection can usually be caused by bacteria, but it can also be linked to the presence of viruses or fungi in the urinary tract. This disease causes symptoms such as pain, burning and urgency to urinate, but in more severe cases blood may also be produced in the urine and inflammation of the prostate in men.
Treatment of urinary tract infection is done according to the cause of the problem, but antibiotics such as amoxicillin are generally used, and the duration of treatment varies according to the severity of the infection. See how treatment with medicines and home remedies for urinary tract infection is done.
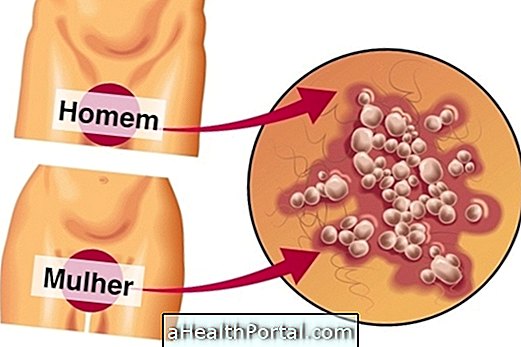
Ringworm
Mycosis in the genital region is also known as tinea cruris and is caused by fungi that can reach the groin, thighs and buttocks. The symptoms of this infection are pain, itching, burning redness and small red blisters on the affected organs.
Treatment of genital mycosis is done with antifungal ointments such as ketoconazole and miconazole, but when the infection is recurrent or when ointment does not eliminate the disease, it may be necessary to take pills, such as fluconazole, to combat mycosis in the groin.
It is important to remember that as soon as the symptoms appear, one should seek the doctor to diagnose the cause of the changes in the genital region and initiate treatment, preventing the progression of the disease and the appearance of complications.
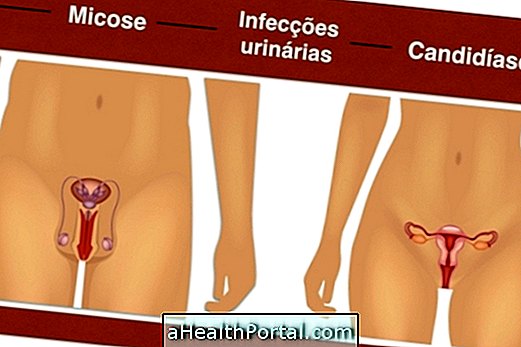
Main forms of contagion
The main forms of contagion of genital infections in diabetics are:
- Lack or excess hygiene in the genital area;
- Do not use a condom during intimate contact;
- Untreated infections in other parts of the body that end up passing into the genitalia.
It is important to note that genital infections are also common in people without diabetes, but diabetics should be more careful because they are more vulnerable to these infections, which can become recurrent and difficult to treat.
How to Prevent Recurrent Infections
To prevent infections from recurring, the diabetic should:
- Keep blood glucose controlled, so that excess blood sugar does not harm the immune system;
- Observe the genital area daily, looking for changes such as redness and blisters on the skin;
- Use a condom during intimate contact, to avoid contagion of diseases;
- Avoid frequent washings with showers in the genital region, so as not to alter the pH of the region and not to favor the growth of microorganisms;
- Avoid wearing very tight or warm clothes throughout the day, as they favor the proliferation of microorganisms in the genitals.
However, by controlling blood glucose and taking the necessary care to avoid infection, it is possible to have a normal life and live well with diabetes.