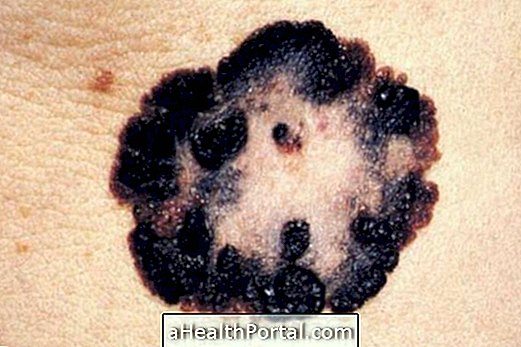
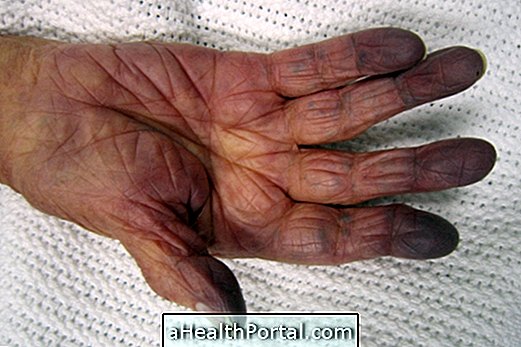
To treat gout, medications such as anti-inflammatories, analgesics, and corticoids are often needed, which are used in acute cases and to prevent seizures.
In addition, some of these drugs can also be used at lower doses to prevent seizures and there are other remedies that help prevent complications caused by the disease, which work by reducing the production of uric acid or promoting its elimination.

1. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, or celecoxib are widely used to alleviate symptoms in acute attacks of gout at higher doses and to prevent future seizures at lower doses.
However these medications can cause gastric side effects such as stomach pain, bleeding and ulcers, especially in people who take these medications daily. To reduce these effects, it is best to take these medicines after meals and your doctor may also suggest taking a stomach shield every day, on an empty stomach, to relieve discomfort.
2. Colchicine
Colchicine is a widely used remedy to treat and prevent gout attacks, as it decreases the deposition of urate crystals and the consequent inflammatory response, thus reducing pain. This medicine may be used daily to prevent seizures, and the dose may be increased during an acute attack. Learn more about this medicine.
The most common side effects that can occur with the use of colchicine are digestive disorders such as diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
3. Corticoids
The doctor may recommend corticosteroids such as prednisone tablets or injectables to reduce pain and inflammation, which are most often used in situations where people can not take other anti-inflammatories such as indomethacin or celecoxib or who can not use colchicine.
The most common side effects that can be caused by the use of prednisone are mood swings, increased blood sugar levels and increased blood pressure. Know that other side effects can be caused by corticodes.
4. Remedies that block the production of uric acid
The most commonly used drug to block the production of uric acid is allopurinol, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, which is an enzyme that converts xanthine to uric acid, lowering blood levels, reducing the risk of onset of seizures. See more about this medicine.
The most common side effects that can be caused by allopurinol are rashes.
5. Remedies that increase elimination of uric acid
One drug that can be used to eliminate excess uric acid through urine is probenecid, which leads to its decrease in the bloodstream. Learn more about this medicine.
The most common side effects that can occur with the use of these medications are rash, stomach pain and kidney stones.