The first trimester pregnancy tests, which should be done up to 13 weeks of gestation, are important for assessing the mother's health, mother's risk of passing on certain diseases to her baby, identifying malformations and the risk of miscarriage.
The full list of the first trimester pregnancy exams includes blood tests, ultrasound, and gynecological examination, which should be performed when requested by the doctor accompanying the pregnancy.
Physical exam
Physical exams in the first trimester of pregnancy are:
- Blood pressure : Should be performed at all prenatal visits because it evaluates the risk of eclampsia, which can lead to early delivery.
- Uterine height : With the woman lying down, the doctor or nurse places a tape measure in the abdominal region to evaluate the growth of the baby.
- Weight : Performed in all consultations to assess how much a woman is fattening during pregnancy because it is not advised to put on too much weight and, in the case of obese pregnant women, the care is greater.
In some cases, one can hear the baby's heart beating with a specific device for this purpose. This device is available for sale at mom and baby products stores or on the internet and is marketed under the name sonar.
Bloodtests
The obstetrician should request these exams at the first prenatal visit. The blood tests to be done in the first trimester of pregnancy are:
- Complete blood count : Used to check for infection or anemia.
- Blood type and Rh factor : Important when the Rh factor of the parents is different, when one is positive and the other is negative.
- VDRL : Used to check for syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease, which if not properly treated can lead to malformation of the baby or miscarriage.
- HIV: It serves to identify the HIV virus that causes AIDS. If the mother is properly treated, the chances of the baby getting contaminated are low.
- Hepatitis B and C : It is used to diagnose hepatitis B and C. If the mother receives the proper treatment, it prevents the baby from being contaminated with these viruses.
- Thyroid : Used to evaluate thyroid function, TSH, T3 and T4 levels, as hyperthyroidism can lead to spontaneous abortion.
- Glucose : Used to diagnose or monitor the treatment of gestational diabetes.
- Toxoplasmosis : Used to check if the mother has had contact with the protozoan Toxoplasma gondi, which can cause malformation in the baby. If it is not immune, it should receive guidance to avoid contamination.
- Rubella : It is used to diagnose if the mother has rubella, as this disease can cause malformation in the baby's eyes, heart or brain and also increases the risk of miscarriage and premature delivery.
- Cytomegalovirus or CMV : It is used to diagnose cytomegalovirus infection, which, when not properly treated, may cause growth restriction, microcephaly, jaundice or congenital deafness in the baby.
In addition, exams to identify other sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can also be done during prenatal care, which can be diagnosed by examination of vaginal secretions or urinalysis. If there is any change in any of these tests, the doctor may request a repeat examination in the second trimester of gestation.
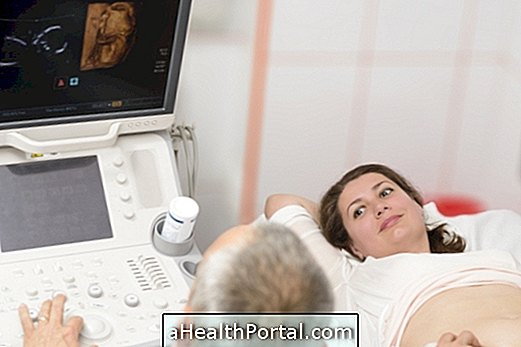
Ultrasound
The first ultrasound examination of pregnancy is a transvaginal ultrasound, which is usually performed between the 8th and 10th week of gestation. It works for:
- confirm pregnancy;
- check that the baby is actually in the uterus and not in the tubes;
- the time of gestation;
- baby's heart rate;
- if they are twins;
- to calculate the expected date of delivery.
In the ultrasound performed at 11 weeks, it is possible to measure the nuchal translucency, which is important to evaluate the risk of the baby suffering from a genetic disease, such as Down Syndrome.
Urine
Urine and uroculture tests are used to diagnose urinary tract infection, which is very common during pregnancy and which, when not properly treated, can lead to premature labor.
Gynecological examination
The gynecological exam is also performed at the first prenatal visit.
In the gynecological exam the obstetrician will evaluate the appearance of the woman's intimate region and will perform the Pap smear, which is used to evaluate infections such as Candidiasis, vaginal inflammation and cervical cancer, which, when not properly treated, can drink.
Useful links:
- Second trimester pregnancy tests
- Nuchal translucency
- Feeding in pregnancy