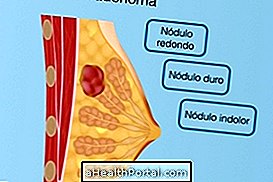
Breast dysplasia, called benign fibrocystic alteration, is characterized by changes in the sinuses, such as pain, swelling, thickening, and nodules that usually increase in the premenstrual period due to female hormones.
Breast dysplasia has a cure because it is not a disease, but only normal changes that occur in the breasts due to the hormones. For this reason, the woman generally does not need treatment because these changes tend to disappear after menstruation.
However, when breast dysplasia causes very severe pain, the treatment, which should be indicated by the mastologist, can be done through analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen or aspiration of the nodules by needle to be emptied. Supplementation with vitamin E can also be prescribed by the mastologist, as it alleviates the symptoms by helping in the production of the hormones in the woman.
Breast dysplasia usually occurs after adolescence, being more frequent in women who do not have children. During breastfeeding, breast dysplasia improves and can occur in menopause, especially if the woman is not undergoing hormone replacement.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of breast dysplasia include:
- Breast pain;
- Swelling of the breasts;
- Hardening of the breasts;
- Breast tenderness;
- Breast nodules. Understand when the lump in the breast can be serious.
These symptoms tend to soften after menstruation due to the drop in hormones.
What are the causes
The causes of breast dysplasia are related to female hormones. Generally, fluid buildup occurs in the breast tissues, causing swelling, tenderness, pain, tightening, and nodules in the breasts.
Can breast dysplasia become cancer?
Benign breast dysplasia rarely develops cancer, however, any woman has a risk of developing cancer for other reasons.
Therefore, it is important to perform mammograms from the age of 40 and breast ultrasound at any age if you notice any nodulation in the breast, or symptoms such as pain, discharge or redness. Also check the signs and symptoms that indicate breast cancer.
Treatment for breast dysplasia
Treatment for breast dysplasia is not always necessary. However, when the symptoms are very strong and uncomfortable, it can be done with hormonal drugs and analgesic and anti-inflammatory medicines like Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, indicated by the mastologist.
In addition, the mastologist can also prescribe a vitamin E supplement to supplement the treatment, as this vitamin helps in the production and balance of the female hormones. Alternatively, the woman can also increase the consumption of foods rich in vitamin E like wheat germ oil, sunflower seeds or hazelnuts, for example. See other foods in: Foods rich in vitamin E.
Surgery for breast dysplasia is usually not indicated, as the nodules need not be removed. However, if they cause too much discomfort, they can be emptied through an ambulatory doctor's puncture.
To relieve pain and symptoms, a woman should avoid salt and caffeine foods such as coffee, chocolates, tea and coke, increase fluid intake, and wear wide bras that support the breasts better.





.jpg)