Second-trimester exams should be performed between the 13th and the 27th week of gestation and are more focused on evaluating the baby's development.
The second trimester is generally quieter, with no sicknesses, and the risk of miscarriage is lower, which makes the parents happier. At this stage, the doctor should ask for some tests to be repeated to make sure that everything is okay with the mother and the baby.
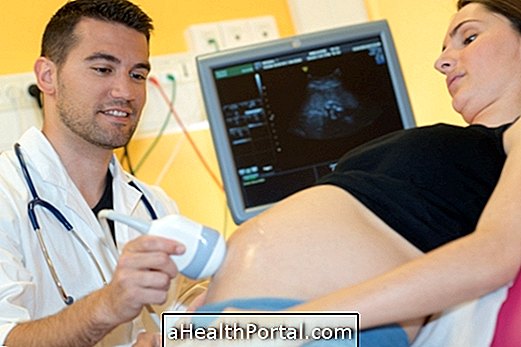
The second trimester pregnancy exams are:
- Blood pressure : Important to evaluate the risk of pre-eclampsia, which can lead to preterm delivery.
- Uterine Height : Checks the size of the uterus, which up to 28 weeks of gestation should be 24 cm.
- Morphological ultrasound : Should be performed between the 18th and 24th weeks of gestation and assess the development of the heart, kidneys, bladder and stomach, the quantity and quality of the amniotic fluid, identify the sex of the baby and may reveal some syndromes and heart disease.
- Urine and uroculture :? It serves to diagnose urinary tract infection, which when not properly treated can lead to premature labor.
- Hemogram : It should be performed at the 24th week of gestation and is used to check if the mother has anemia.
- Glucose : Also at the 24th week, the glucose test should be performed, which evaluates blood glucose after taking a sugary liquid called destrozol, which is important to check if the mother has gestational diabetes.
- VDRL : Serve to check for syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease, which if not properly treated can lead to malformation of the baby or abortion.
- Toxoplasmosis : Used to check whether or not the mother is immune to toxoplasmosis and for the doctor to remember food care if the mother is not immune.
- Fetal Fibronectin : Consists of withdrawal of vaginal secretions. It should be performed at the 22nd week of gestation and assess the risk of preterm delivery.
The doctor may indicate or request tests such as urea, creatinine and uric acid, liver enzymes, electrocardiogram and ABPM for some pregnant women. In addition, urine tests or assessment of vaginal discharge and cervix may also be prescribed to identify other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. See the 7 most common STDs in pregnancy.
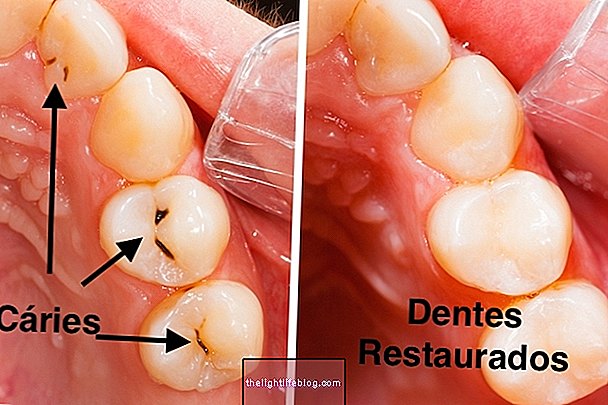
In the second trimester of pregnancy, the pregnant woman should go to the dentist to evaluate her oral health and treat cavities or other dental problems, as well as receive guidance on bleeding gums, which is very common during pregnancy.
See also the third trimester pregnancy exams.