Water in the lung, also known as pulmonary edema, is characterized by the presence of fluid inside the lungs, which prevents gas exchange. Pulmonary edema can occur mainly due to heart problems, but can also be due to drowning, lung infections, exposure to toxins or smoke and high altitudes. Learn what can cause water in the lung and how to treat it.
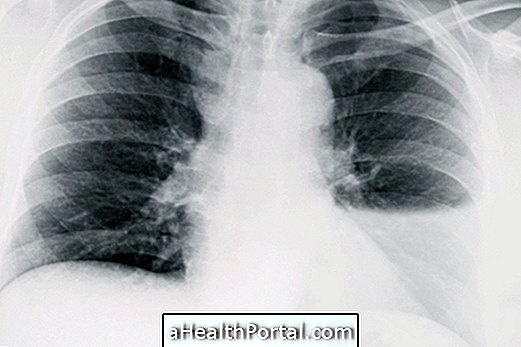
The diagnosis is made mainly through the chest X-ray associated with the analysis of the symptoms presented by the person, which may arise suddenly or in the long term.
Symptoms of water in the lung
Symptoms of water in the lung include:
- Intense difficulty in breathing;
- Noisy breathing;
- Pale skin;
- Mucous purples (Eyes, lips);
- Not being able to lie down because of the lack of air;
- Anxiety;
- Cough, which may contain blood;
- Swelling of the legs or feet;
- Chest tightness.
Treatment should be started as soon as possible, and is designed through regularization of breathing, removal of water in the lung and cessation of the causative agent. This can be achieved by placing a drain in the lung, using medications and in some cases cardiac surgery when there is this need. Learn more about treatment for lung water.
How to identify
Confirmation of the diagnosis of water in the lung is made when the person, in addition to the characteristic symptoms of the condition, has a blurred spot around the lung on the X-ray examination, and up to 75 mL of water in the lung can be identified.
In addition to the X-ray examination, pulmonary and cardiac auscultation, electrocardiogram, heart enzyme dosage, blood pressure measurement and arterial blood gas analysis may be requested. Understand how the arterial blood gas test is done.