Cysts are types of nodules filled with a liquid, semi-solid or gaseous content, as species of pockets, and are, in most cases, benign and asymptomatic. They can develop anywhere in the body, most commonly arising in organs such as breast, thyroid, ovaries, liver or joints, for example.
There are several causes that cause cysts such as infections, trauma, obstruction of the sebaceous glands, or even a matter of genetics. Usually do not need treatment, except in situations that need further investigation or when they have suspicious features of gravity, can be aspirated with specific needles or removed with surgery.
There are several types of cysts, which must be evaluated and identified by the doctor. However, we will make a brief summary of the most frequent ones here:
1. Ovary cyst
The cyst in the ovary, most of the time, is benign, posing no risk to a woman's health. They usually arise due to hormonal changes present throughout the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause or with use of certain hormonal medications, for example.
Most of the time, simple cysts in the ovary do not need any treatment, and may regress spontaneously, however, there are situations in which they need to be removed with surgery, such as when they grow too large and cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, when they present some type of complication, such as breaking or twisting, or when the ultrasound shows suspicious features of malignancy, such as rapid growth, contain solid parts or blood vessels, for example.
There are several types of cyst in the ovary, see which, how to identify and treat.
2. Naboth cyst
Naboth's cyst may form in the cervix due to the accumulation of mucus released by the Naboth glands when their ducts become obstructed and prevent the passage of mucus.
These cysts are common in women of childbearing age and are not a cause for concern as they are usually benign. However, these nodules do not always heal spontaneously, and treatment with electrocautery may be indicated. Learn more about this type of cyst.
3. Baker's cyst
Baker's cyst appears in the knee joint, being seen as a lump located in the back of the knee. It arises due to fluid accumulation of the joint, and although it does not always provoke symptoms, it can cause pain and stiffness in this place, making it difficult to move the knee.
Usually this cyst arises due to knee problems that cause lesions or wear on your structures, such as arthrosis, meniscus injury, rheumatoid arthritis or gout, for example. Learn how to identify this cyst and what treatment.

Sebaceous cyst
The sebaceous cyst is a type of lump that forms under the skin, filled with keratin and other materials derived from the skin, also called sebum, white in color, semi-solid and soft to the touch.
This cyst usually forms after trauma to the skin or inside hair follicles, is benign and does not need any treatment. However, if it becomes uncomfortable, grows too much or causes pain due to inflammation or infection, removal is usually done by simple surgery, usually by the dermatologist. See what the surgery consists of.
5. Cyst in the kidney
The simple cyst in the kidney is usually benign and does not usually cause symptoms, requiring only doctor follow-up.
However, if the ultrasound examination shows suspicious signs of a serious injury, such as an abscess or cancer, the doctor should indicate further investigation, with a CT scan, magnetic resonance imaging and, if necessary, a puncture for analysis of its contents. See more about cyst in the kidney.
6. Pilonidal cyst
The pilonidal cyst is characterized by a pouch consisting of material of sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as pieces of skin and hair, which develops usually at the end of the spine, just above the buttocks, generating symptoms such as pain, swelling, heat and cracks in the skin.
The main form of treatment is your withdrawal through surgery. Learn more about how to form and how to treat this cyst.

7. Bartholin's cyst
Bartholin's cyst occurs due to an obstruction of the Bartholin's gland, which is located in the anterior part of the vagina and which is responsible for lubricating it during intimate contact.
This cyst is usually painless, causes no symptoms and can heal without treatment, unless the cyst becomes inflamed or infected, and may be indicated the use of anti-inflammatories, antibiotics or even surgery. Learn what can cause the appearance of Bartholin's cyst.
8. Synovial cyst
Synovial cyst is a benign tumor, filled with clear fluid, which forms near joints, especially of the wrist, but also knees, ankles, or feet.
Although its exact causes can not be explained, it can be associated with trauma, repetitive strain injury or joint defect, and although it does not always cause symptoms, it can cause pain, loss of strength and sensitivity at the site, and aesthetic complaints. See more about synovial cyst and when treatment is needed.
9. Arachnoid cyst
The arachnoid cyst is a collection of cerebrospinal fluid between the membranes that cover the brain, and is usually, in most cases, congenital, that is, to be born with the baby.
Usually these cysts are asymptomatic, however, if they grow they can cause damage to the brain, and therefore need treatment, which is done with surgery. See more about symptoms and treatment.
10. Liver cyst
The simple cyst in the liver, in most cases, produces no symptoms or any changes in the body. In addition, it is usually not severe and is not a sign of cancer, but should be monitored and if it increases in size or appear suspicious characteristics of malignancy on examination, the doctor may indicate specific treatments. Learn more about liver cysts.

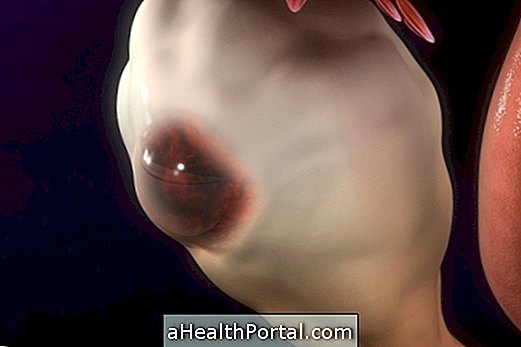
11. Cyst in the breast
Cysts in the breast are usually asymptomatic and benign, and usually appear in women aged 15-50 years. Most of the time, it is only necessary to follow the injury, however, when they provoke pain, discomfort, grow over time or when they present other characteristics suggestive of malignancy, they should be punished by the doctor for a better evaluation of its contents. Know when the cyst in the breast is at risk of becoming cancer. .
Possible causes
The cyst can be triggered by several factors, depending on your type and location. Some of the most common causes are:
- Infections;
- Defects in baby development;
- Genetic factors;
- Tumors;
- Defects in cells;
- Inflammatory diseases;
- Injury or trauma to affected tissues;
- Blockage of glands.
In some cases, they may also develop due to injury or trauma to the tissues of the affected region, which is common in cysts that arise in the joint region, for example.

Can cysts turn cancer?
Usually the cysts are benign nodules and may disappear even without treatment. However, they should always be watched because, in some cases, they may grow large or have suspicious characteristics, such as having a solid content, requiring further investigation and doctor-directed treatments.