To get the first aid for diabetics you need to know if it is an episode of excess blood sugar or lack of sugar. Therefore, if possible, it is important to check with a device to measure the amount of blood sugar, what the value of blood glucose.
In addition, it is also important to know what first aid in other situations that can happen in the day-to-day and that pose a greater risk of consequences for the diabetic, such as having a skin wound or twisting the foot, for example.
What to do when sugar is high
In cases where sugar is high in the blood, called hyperglycemia, that is, when the value of the device is above 180 mg / dL fasting or above 250 mg / dL at any time of the day, or the victim is confused, thirst or apple breath, it is due to:
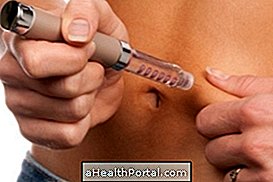
- Look for any insulin syringes the victim may have for emergency situations;
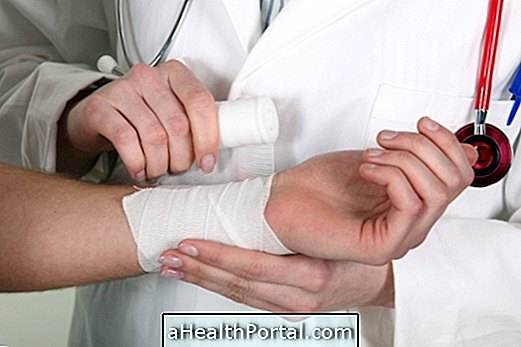
- Inject the syringe in the region around the navel or the upper arm, making a fold with your fingers, holding it until the end of the injection, as in image 1;
- If 1 hour has elapsed, the sugar value remains the same, call for medical help immediately by calling the number 192 or take the victim immediately to the hospital.
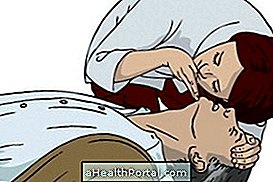
If the victim is unconscious, place it in the lateral safety position, as shown in figure 2, while awaiting the arrival of medical help.

What to do when sugar is low
Even when sugar is low in the blood, called hypoglycemia, that is, when the blood sugar level is below 70 mg / dL or the person has symptoms such as tremors, cold skin, or fainting, it is important to:
- Offer something sweet to eat, such as 1 tablespoon full or 2 packets of sugar with a loaf of bread;
- If blood sugar does not increase or symptoms do not improve within 30 minutes, give the victim sugar again (if conscious);
- If after 30 minutes the sugar remains the same, call for medical help immediately by calling the number 192 or taking the victim to the hospital immediately;
- If victim is unconscious, place in safety position while waiting for medical help.
In cases where blood sugar does not rise, emergency medical help is needed for the victim to receive medicine through the vein.
What to do when a skin sore
When the diabetic is injured, it is important to take good care of the wound, because even if it is small and superficial, the wound is more likely to present complications such as ulcers or infections, especially when it occurs in moist or muffled places such as feet, skin or groin, for example.
Read how you should properly care for skin wounds in case you have diabetes.
In addition to taking care of the wound, it is also essential to be alert to some signs that indicate the development of these complications, such as the appearance of redness, swelling, severe pain or pus in the area. In these cases, it is recommended to go to the general practitioner.
When the wound is very small but it takes more than 1 month to heal, it is advisable to go to a nursing consultation to evaluate the need for a more specialized treatment, with dressings that favor healing.
How to avoid complications in the wound
During treatment it is important to take care to avoid infections, due to:
- Use clean towels to dry the affected skin area;
- Avoid contact with domestic animals;
- Avoid locations with sand or earth;
- Avoid tight clothing or shoes on the bruise.
Thus, the ideal is to always keep the wound clean, dry and away from situations that may worsen the wound, especially until healing is complete.
What to do if you twist your foot
If the diabetic twists the foot or other joint, one should stop practicing physical activity and avoid forcing the affected place, avoiding walking for a long time and climbing stairs, for example.
In addition, keep your foot elevated to promote circulation and put ice in the affected area for 20 minutes, 2 times a day, remembering to wrap the ice in a damp cloth to avoid burning the skin.
The twist usually causes swelling and pain, and leaves the region warmer and with purple spots. In severe cases, where there is severe pain and swelling that does not improve, the physician should be sought to assess the severity of the injury and check for a fracture.
Warning signs to go to the doctor
The doctor should be sought when:
In case of high sugar
- Capillary glycemia greater than 180 mg / dL for more than 1 hour, fasting;
- Capillary glycemia greater than 250 mg / dL for more than 1 hour after eating;
- The patient is unconscious. In this case medical help should be called promptly by calling 192.
In case of low sugar
- Capillary glycemia less than 70 mg / dL for more than 30 minutes;
- The patient is unconscious. In this case medical help should be called promptly by calling 192.
In case of skin sores
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Presence of pus in the wound;
- Increased redness, swelling and local pain;
- Worsening of wound healing process;
- Loss of sensitivity around the wound or tingling;
- Presence of sweat and shivers in the body.
These signs indicate that the wound site may be infected, with a higher risk of worsening of the wound and complications such as ulcers.
In more severe cases, when these signs are ignored and proper treatment is not done, the affected tissue may undergo necrosis, which occurs when the region does not receive enough oxygen and the tissues die, and it may be necessary to amputate the affected limb.
Learn more at:
- First aid for hypoglycemia
- What to Eat in Diabetes