An abdominal hernia is characterized by a bulging of some organ of the belly out of the body that generally does not cause symptoms, but can cause pain, swelling and redness in the place, especially when there is an incarceration or twisting of the organs that are within the hernia .
This hernia can appear in people of any age by genetic weakening of the wall that covers the abdomen, or after some effort, such as coughing or lifting an excessive weight, and is therefore more common in the groin and navel, or even even after surgery at that location.
Treatment for the abdominal hernia is done by surgery to replace that part of the organ behind the abdominal muscles. The surgery is simple without the need for general anesthesia and usually the person stays in the hospital for only 1 day.
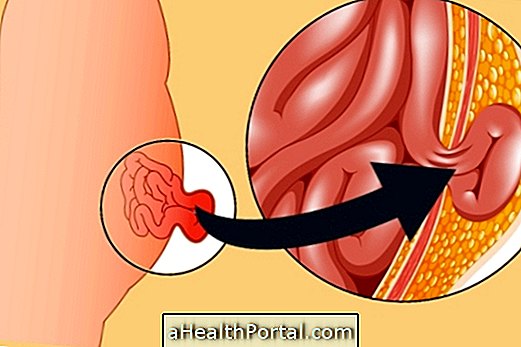
Main symptoms
The presence of an abdominal hernia is noticed due to the presence of a swelling or a lump in the belly region, especially in the region above the navel, inside the navel and in the groin. This swelling is formed when the contents of the belly, usually intestine, can overcome the muscle of the belly, forming a hernial sac.
Generally, the contents of the hernial sac can go in and out freely, without causing symptoms, or cause a slight nuisance. However, when the orifice of the passage of the organs becomes narrower, there is the so-called incarcerated or strangled hernia, which may present symptoms, such as:
- Severe pain at the site of the hernia or abdomen;
- Swelling and redness at the hernia site;
- Nausea and vomiting.
This condition is serious, and should be treated with surgery as soon as possible, due to the risk of lack of blood circulation to the organs, there being a risk of inflammation, perforation and infection, which is necrosis.
Surgery for abdominal hernia
The main treatment for hernias is surgery, however, in some cases, they may regress on their own, as in the case of small hernias or hernias in the baby, especially the umbilical.
The surgery is performed in a surgical center, with local or spinal anesthesia, and can be done with the opening of the abdomen or by videolaparoscopy, in a procedure that lasts about 1 hour. Thus, the organs are pushed and reintroduced into the abdomen, and the opening is closed with suture.
In some cases where the belly muscles are very weakened, it may be necessary to place a screen to strengthen the protection.
How is recovery
The postoperative period of abdominal hernia surgery usually occurs with a rapid recovery, and within 1 to 2 days, the patient has been discharged from the hospital. The recommendations are:
- Use of pain-relieving analgesic or anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a physician;
- Do not carry out efforts like driving or carrying weight for 7 to 10 days;
- Return to the reassessment consultation with the surgeon in 7 days;
- Perform more intense physical activities, such as sports, after 1 month.
Most of the time, the hernia gets cured with surgery and, therefore, there is a very small risk of recurrence.
What causes abdominal hernia
The hernia occurs when there is some weakening of the belly tissue, which may be genetic, or which may arise after an increase in pressure inside the belly, as happens after an effort, due to obesity or pregnancy, for example.
The main types of abdominal hernia are:
- Inguinal, in the groin area, which is the most common type. Learn how to identify and treat an inguinal hernia;
- Epigastric, which is above the navel, at the junction between the muscles of the abdomen;
- Umbilical, is the most common in babies, and generally regresses without needing surgery in the first years of life. Here's what to do if I had an umbilical hernia;
- Incisional, it happens at the site of some old surgery, due to the weakening of the place where the suture was made.
To diagnose the abdominal hernia, the doctor can perform a physical examination that evaluates the barium swelling, but the confirmation is made by an ultrasound examination of the abdomen.