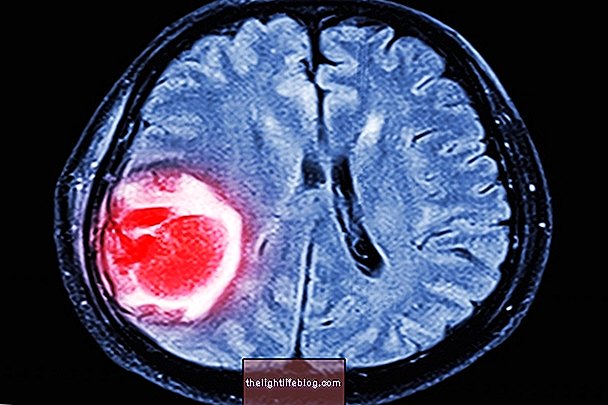
Tumor symptoms in the brain depend on the size, speed of growth and location of the tumor that, although it may appear at any age, usually appears mostly after age 60.
Usually benign brain tumors, such as meningioma or glioma, grow slowly and do not always need treatment, because often the risk of surgery is greater than the tumor's bad effects. See what are the major types of brain tumor.
However, when tumors are malignant, cancer cells proliferate rapidly and can reach various regions of the brain. These cancer cells may also appear as metastases from other foci of cancer, such as lung or breast cancer. To differentiate, see the signs of cerebral aneurysm.

General Symptoms
The brain tumor, regardless of the region of the affected brain, causes general symptoms such as headache, blurred vision, convulsions, nausea, vomiting, poor balance, changes in mood and behavior, numbness or weakness in a part of the body, apathy and drowsiness.
However, it is important to remember that these symptoms can also be caused by other diseases, such as migraine, multiple sclerosis and stroke, and it is necessary to see the doctor to have tests done to identify the cause of the symptoms.
Specific symptoms by affected region
In addition to the general symptoms, the tumor in the brain can cause specific symptoms that vary according to the location and size of the tumor:

| Region of the affected brain | Main symptoms |
| Frontal wolf |
|
| Parietal wolf |
|
| Temporal wolf |
|
| Occipital wolf |
|
| Cerebellum |
|
The intensity of the symptoms varies according to the size of the tumor and cell characteristics, whether malignant or benign. In addition, factors such as age and general health may influence the severity and evolution of symptoms.
How is the diagnosis made?
In the presence of one or more symptoms, one should seek the neurologist for more specific diagnostic tests to be performed, such as magnetic resonance or computed tomography, because the earlier the tumor is identified, the easier and more efficient the treatment will be. See how the MRI is done.
In addition, if any lump is detected in the examination, but it has not been clear whether it is malignant or benign, the doctor may order a biopsy of the tumor so that the cells are evaluated in the laboratory and can determine the best form of treatment. Learn how treatment for the brain tumor is done.







.jpg)