Brain contusion is a serious brain injury that usually occurs after a severe head injury caused by a direct and violent impact on the head, such as what happens during traffic accidents or high-altitude falls, for example.
Generally, brain contusion arises in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain because they are places in the brain that are easier to beat against the skull, causing bruising in brain tissue.
Thus, depending on the severity of the injury and taking into account brain sites where a bruise is most frequent, it is possible to develop sequelae, such as memory problems, attention difficulties or changes in emotions, especially during treatment, when the brain is still not fully recovered.
However, not all head trauma causes brain concussion, which can only lead to the development of a concussion, which is a less serious problem, but which must also be quickly diagnosed and treated. Learn more at: Brain Concussion.
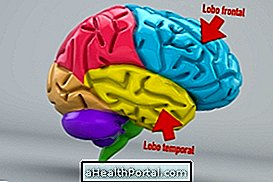

How to tell if you have a brain injury
Brain contusion usually can not be seen with the naked eye and therefore must be diagnosed through examinations such as CT or MRI, for example.
However, some signs and symptoms that may indicate the development of a contusion include:
- Loss of consciousness;
- Confusion;
- Sudden vomiting;
- Frequent nausea;
- Dizziness and severe headache;
- Excessive weakness and tiredness
These symptoms when they appear after a head trauma should be evaluated as soon as possible in an emergency room to confirm the diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
In the more severe cases, where skull fractures occur, the chances of having a brain injury are very great, but the diagnosis should always be confirmed with CT and MRI scans at the hospital.
How To Treat Brain Injury
Treatment for brain injury should be started as soon as possible in the hospital with a medical evaluation done by a neurologist because, depending on the results of the tests and the type of accident that led to the brain injury, treatment may vary.
Most brain contusions are minor serious problems and can only improve with rest and use of remedy painkillers, such as Acetominofeno or Paracetamol, to relieve pain. Anti-inflammatories such as aspirin or ibuprofen should be avoided because they increase the risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
However, in the most severe situations where the bruise causes brain hemorrhages or swelling of the brain tissue, surgery is required to remove excess blood or remove a small part of the skull to reduce the pressure to allow the brain to heal.