Food intolerance is when adverse reactions occur to food, such as intestinal problems, respiratory problems, blemishes and itchy skin. Although the symptoms are the same, food intolerance is different from food allergy because in allergy there is also a reaction of the immune system with antibody formation, and can cause more severe symptoms than in food intolerance. To understand better, see: Difference between allergy and food intolerance.
The treatment of both intolerance and food allergy is to remove the food that causes the problems from the diet. The following is how to discover the presence of eating disorders:
1. Watch for symptoms
One should be aware of the symptoms and identify if they appear after ingesting any particular food. The main symptoms of food intolerance are:
- Abdominal pain;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Gases;
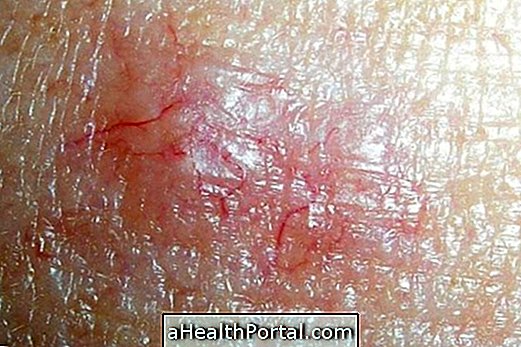
- Itching in the body;
- Red spots on the skin;
- Cough.



These symptoms may appear soon after eating the food or for more than 24 hours afterwards, and their intensity varies according to the amount of food that has been consumed.
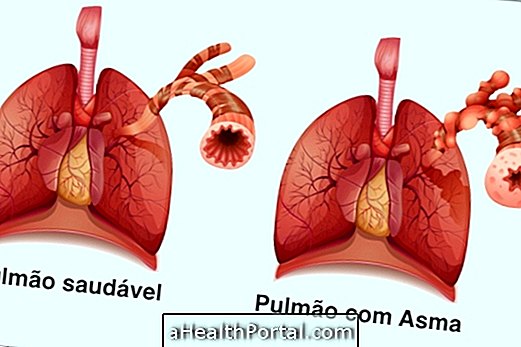
On the other hand, food allergy symptoms occur more quickly and are more severe than intolerance, and can also cause rhinitis, asthma and bloody stools. See more details to clear the question of what can be, in: Learn about the differences between intolerance and food allergy.
2. Identify the food causing intolerance
The next step is to try to identify which food is causing the symptoms of food intolerance. The most common foods that cause intolerance or food allergy are: egg, milk, crustaceans, gluten, chocolate, peanuts, nuts, tomatoes and strawberries. Preservatives and dyes used in industrialized products such as pickled fish and yogurts can also cause food intolerance.
3. Make the diagnosis
To confirm the presence of food intolerance, one should do tests to diagnose which food is doing badly and whether it is intolerance or food allergy. Usually the diagnosis is difficult and can go through the following phases:
- Evaluation of the history of symptoms: when they started and what are the symptoms;
- Food diary: one should write all food eaten and symptoms that appeared during 1 or 2 weeks of feeding;
- Blood tests: evaluate if there are alterations of the immune system that characterize the presence of the allergy;
- Stool examination: check for blood in stool, as allergies can cause lesions in the intestine that cause bleeding;
- Elimination of food from the diet: the food that causes intolerance should be withdrawn from the diet and checked for improvement of the symptoms;
- Food challenge: The food that causes intolerance is put back into the diet to see if the symptoms reappear.
Once identified, the food causing intolerance should be withdrawn from the diet to prevent the reappearance of symptoms.


What are the most serious food problems
The most serious food problems involving food intolerances are phenylketonuria and galactose intolerance, as they can cause delay in the physical and mental development of the baby. In addition to these diseases, cystic fibrosis is also a genetic disorder characterized by difficulty in digesting and absorbing food, and can cause malnutrition and delayed growth.
See the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment for these diseases in:
- What to eat in galactose intolerance
- Understand more about what Phenylketonuria is and how it is treated
- How to know if your baby has cystic fibrosis