The vitamin D test aims to check the concentration of vitamin D in the blood, since this vitamin is important to regulate the levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood. Learn more about what vitamin D is for.
This test is usually ordered by the physician to monitor replacement therapy with vitamin D or when there are signs and symptoms related to bone decalcification, such as pain and muscle weakness, for example, being most often requested along with the dosage of calcium, PTH and phosphorus in the blood. Understand how the blood phosphorus test is done.
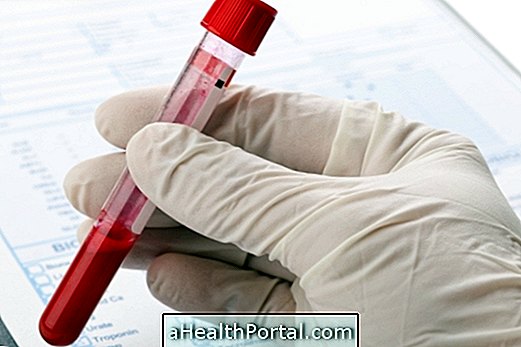
What is it for
The vitamin D test is mainly done to diagnose vitamin D deficiency, in addition to hypervitaminosis D. However, the doctor may also request this examination when there are signs and symptoms of bone decalcification, since vitamin D is one of the factors responsible by regulating the concentration of calcium and phosphorus, besides promoting the mineralization of the bones.
This test is also required to monitor vitamin D replacement therapy and to assist in the differential diagnosis of rickets, osteoporosis, and osteomalacia, which is a disease characterized by brittle and brittle bones in adults. Learn more about osteomalacia.
How the exam is done
To perform the exam, no preparation is necessary. The examination is done by withdrawing a small amount of blood, which is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Vitamin D is produced from a substance derived from cholesterol in the skin, which when stimulated by ultraviolet light from the sun, is converted to cholecalciferol, known as vitamin D. Vitamin D produced undergoes metabolization in the liver, turning into 25- hydroxyvitamin D, which in the kidneys under the influence of parathyroid hormone is converted to 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D, which corresponds to the active and stable form of vitamin D and is responsible for increasing the absorption of calcium in the intestine and, consequently, increasing the concentration of calcium in the blood.
Both forms of vitamin D are dosed, the 25-hydroxyvitamin D dosage being most commonly performed to identify vitamin D deficiency, whereas 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D is usually required for people with kidney disease.
What do the results mean?
From the results of the dosage of 25-hydroxyvitamin D it is possible to indicate if the person has enough, insufficient or is deficient in vitamin D. The reference values of vitamin D are:
| Meaning | Reference value |
| Deficiency | Below 10 ng / mL |
| Insufficiency | Between 10 and 30 ng / ml |
| Sufficiency | Between 30 and 60 ng / ml |
| Toxicity | Above 100 ng / mL |
Decreased vitamin D values
Decreased vitamin D values indicate hypovitaminosis, which may be due to poor sun exposure or low intake of foods rich in vitamin D or its precursors, such as egg, fish, cheese and mushrooms, for example. See other foods rich in vitamin D.
In addition, diseases such as hepatic steatosis, cirrhosis, pancreatic insufficiency, inflammatory disease, rickets and osteomalacia and diseases that occur with inflammation in the intestine can lead to vitamin D deficiency or deficiency. Know the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
Increased amounts of vitamin D
Increased vitamin D values are indicative of hypervitaminosis, which may occur due to prolonged exposure to sunlight or vitamin D intoxication, for example. Learn how to sunbathe to produce enough vitamin D.