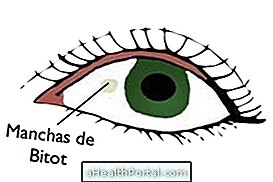
Bitot's spots are grayish-white, oval, foamy, irregularly shaped spots on the inside of the eyes. This spot usually arises due to the lack of vitamin A in the body, which leads to an increase in the concentration of keratin in the conjunctiva of the eye.
Lack of vitamin A is usually characteristic of a condition called xerophthalmia or nocturnal blindness, which is an inability to produce tears and difficulty seeing, especially at night. Thus, Bitot's spots generally correspond to one of the clinical manifestations of xerophthalmia. Understand more about xerophthalmia and how to identify it.

Main symptoms
In addition to the appearance of white-gray spots on the inside of the eye, there may also be:
- Decreased lubrication of eyes;
- Night blindness;
- Higher predisposition to eye infections.
The diagnosis of Bitot's spots can be done through a biopsy of the injured tissue and by researching the amount of vitamin A in the blood.
Possible causes
The main cause of the appearance of Bitot's patches is vitamin A deficiency, which can occur either by reducing foods containing this vitamin or due to situations that make it difficult for the body to absorb the vitamin, such as malabsorption syndrome, for example .
However the spots may also appear as a consequence of the inflammation of the conjunctiva, known as conjunctivitis. See what types of conjunctivitis are.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment is usually done with the aim of eliminating the cause of the Bitot's spot, and the doctor may recommend the use of vitamin supplementation and increased consumption of foods rich in vitamin A, such as liver, carrot, spinach and mango . See what foods are rich in vitamin A.
In addition, the use of specific eye drops may be indicated by the ophthalmologist to decrease corneal dryness. Find out what the types of eye drops are and what they are for.