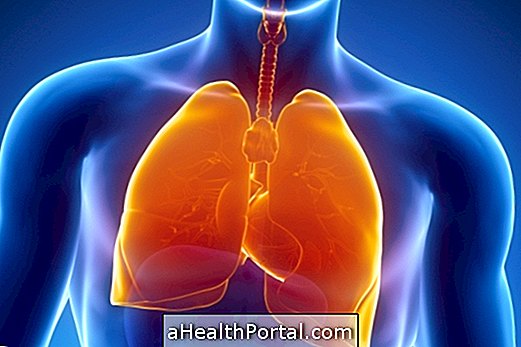
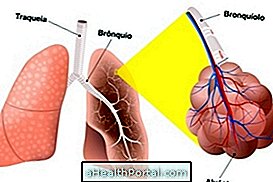
Pulmonary atelectasis is a respiratory complication that prevents the passage of sufficient air due to the collapse of the pulmonary alveoli. This usually happens when there is cystic fibrosis, tumors in the lung or when the lung gets full of fluid due to a strong chest stroke, for example.
Depending on how many alveoli are affected, the feeling of shortness of breath may be more or less intense and therefore the treatment may also vary according to the intensity of the symptoms.
However, in any case, if atelectasis is suspected, it is recommended to go to the hospital quickly, to confirm the diagnosis and to start the most appropriate treatment, since if the lung is still affected, life may be life-threatening.

Possible symptoms
The most common symptoms of atelectasis include:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Rapid, shallow breathing;
- Persistent cough;
- Constant chest pain.
Usually atelectasis happens in people who are already hospitalized as a complication of health, however, if you feel any of these symptoms it is very important to quickly notify a doctor or nurse.
How to confirm the diagnosis
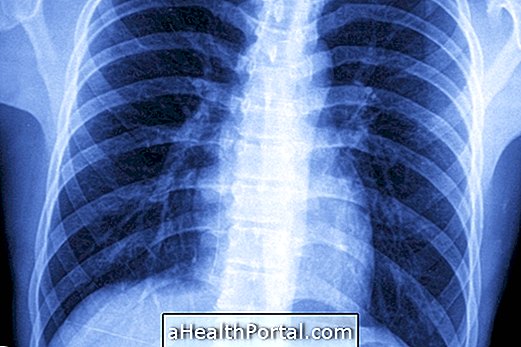
In case of suspected atelectasis, the doctor may order several tests, such as chest x-ray, tomography, oximetry and bronchoscopy, to confirm the presence of collapsed pulmonary alveoli.
What can cause atelectasis
Atelectasis usually occurs when a lung pathway is obstructed or there is too much pressure outside the alveoli. Some problems that can cause this type of change are:
- Accumulation of secretions in the respiratory tract;
- Presence of a foreign object in the lung;
- Strong bangs on the chest;
- Pneumonia;
- Presence of fluid in the lung;
- Pulmonary tumor.
In addition, atelectasis also arises after surgery, because the anesthetic effect may lead to the collapse of some alveoli. However, in such cases a ventilator is used to ensure that air enters properly into the lungs.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for atelectasis is done according to the cause and the intensity of the symptoms, and in milder cases neither therapy nor any type of therapy may be necessary. If the symptoms are more intense, breathing exercises may be used to try to open the lung alveoli, such as coughing, breathing in a few times or giving slight touches on the affected area to release the accumulation of secretions.
In more severe cases, surgery may be needed to clear the airway or even to remove the affected part of the lung, allowing it to re-function properly.
Whenever there is an identifiable cause of atelectasis, such as tumor or fluid in the lung, the problem should always be treated to ensure that atelectasis does not recur.