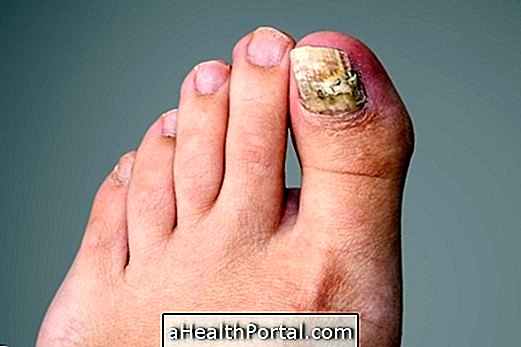
The footworm is a small parasite that enters the skin, especially in the feet, where it develops rapidly. It is also called sand-creatures, pigs, dogworms, jatecuba, mtacanha, sand fleas or tunga, for example, depending on the region.
This is a skin infection caused by a small flea, called Tunga penetrans, which is able to infiltrate and live for several weeks on the skin, causing a small injury that can ignite and cause symptoms such as pain, itching and redness.
To treat this infection, it is necessary to remove this parasite from the skin, preferably at a health clinic, with a sterile needle; however, camphor-based creams or salicylated vaseline may be used to facilitate treatment or drug options such as the thiabendazole or ivermectin in tablet or ointment, for example, doctor-directed in cases of necessity.
However, the only way to control and prevent new infections is through prevention, avoiding walking barefoot on sand and mud, and not going to places with garbage and poor sanitation.
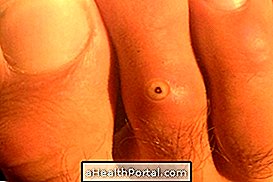

Main symptoms
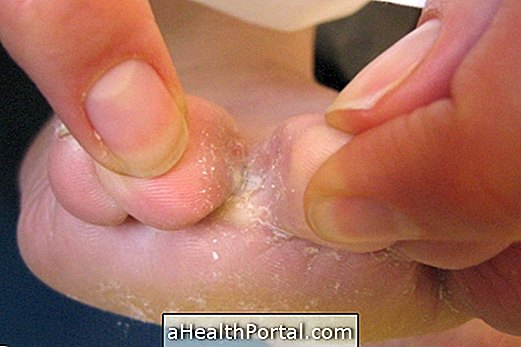
The infection causes lesions that occur mostly on the soles of the feet, around the nails and in the spaces between the fingers, although it also happens in the hands or elsewhere in the body.
Already within the first 30 minutes after penetrating the skin, the parasite produces early symptoms, such as a red spot of about 1 mm and mild local pain. Then the symptoms that can arise on the skin over the days are:
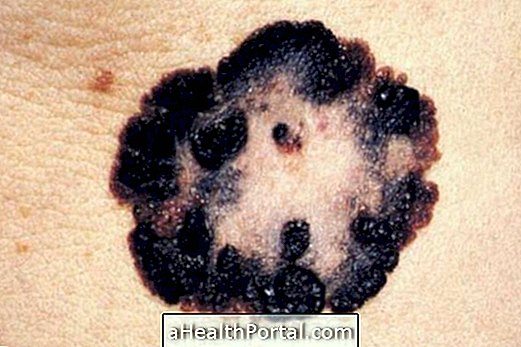
- Eruption in the skin, with a black dot in the center and white around it;
- Itching;
- Pain and discomfort;
- Presence of transparent or yellowish secretion if there is inflammation or local infection.
After about 3 weeks, and after having expelled all eggs, the parasite may spontaneously exit or be killed and eliminated by the immune system, however it may leave residues that may remain for months on the skin.
To diagnose and confirm the presence of the foot bug, the doctor or nurse should only assess the characteristics of the wound, and no further examination is necessary.

How to handle
The places where the eggs and parasites that cause footbaths are mainly the soils with sand and low luminosity, as near to backyards, gardens, sheds or mounds of dung. The flea measures about 1 mm and may also be on the hair of dogs and rats, feeding on their blood.
When the female is full of eggs, it seeks to penetrate the skin of other host animals, such as the pig or people, where it is infiltrated, leaving the posterior part out, which gives rise to the black spot of the lesion, in order to eliminate the eggs and feces.
During this period, which lasts 2 to 3 weeks, the female can reach the size of a pea due to the development of the eggs, which are being released to the outside. After this, the insect dies, its shell is expelled and the skin heals again, and the eggs deposited in the environment become larvae in three to four days, which will grow and become new fleas that can re-infect more people.

How to remove the foot bug
Even if the parasite is only temporarily in the skin, it is very important that the treatment be done, both to avoid complications such as bacterial infections, loss of nails, formation of ulcers and deformities in the fingers, and to prevent new eggs from being released into the environment, and can infect others.
The treatment options are:
- Removal of the foot bug, with a cutting needle or scalpel, which is the main form, made in a health post, after cleaning the wound and sterilization of the materials;
- Use of medicines, such as thiabendazole or Ivermectin, prescribed by the doctor, especially when there is a large number of foot-wearers in the body;
- Use of ointments based on camphor or salicylated vaseline or with the same active principle as dewaxes.
The doctor may direct the use of antibiotics, such as Cephalexin, in case of infection by bacteria. In addition, vaccination for tetanus is indicated in all cases of foot-and-mouth disease, since skin perforation may be a gateway to the bacterium of this disease.


How to avoid picking up
To prevent foot-wear, you should always wear closed-toed shoes in sand and where many pets, such as dogs and cats, pass through.
In addition, it is important to take pets to the vet to assess if they are infected with the footworm's flea, and initiate appropriate treatment so that the disease does not pass to people.
Another common disease that is contracted from animals infected by worms is the geographic bug, which causes wounds, with redness and intense itching, especially in the feet. Learn more about this infection in geographic bug symptoms.