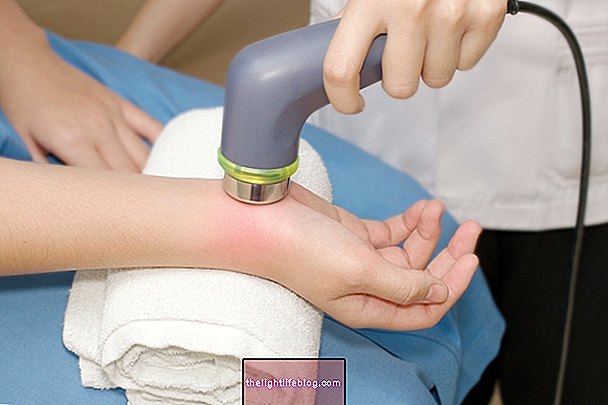
The infiltration consists of applying an injection with corticosteroids, anesthetics or hyaluronic acid to treat lesions, inflammations or reduce pain. This procedure is most often done on joints such as knee, spine, hip, shoulder or foot, although it can also be done on muscles or tendons.
The purpose of infiltration is to treat the disease where the injury or inflammation occurs, especially in the most severe cases or when there has been no improvement with other tablet or topical treatments, being very used in the treatment of arthrosis, as well as helping to recover tendinitis, epicondylitis or bruises that occur through sports practices, for example.

What is it for
Although they can be done in various places in the body, such as muscles and tendons, infiltrations within the joints are the most common. They can be made with different types of medications, which are chosen by the doctor according to the main purpose, which may be to reduce pain, decrease inflammation or increase the amount of synovial fluid, which is a liquid that acts as a kind of inside the gaskets.
In this way, in addition to relieving pain, infiltrations are useful to combat the progression of joint wear, decrease swelling and improve joint function, enabling a better quality of life.
Some medications that may be used for infiltrations include:
1. Anesthetics
Anesthetics are usually applied in case of severe or chronic pain and usually promote pain relief soon after its application. Due to the immediate and temporary effect, anesthetics are often used to confirm that the source of the pain is actually inside the joint, to better define the treatment or to schedule surgeries, for example.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are potent anti-inflammatory drugs and can be applied alone or together with an anesthetic to combat pain and inflammation within a joint. A steroid infiltration is usually done every 3 months and it is not recommended to make excessive applications in the same place as this may increase the risk of side effects and be harmful.
Some of the major corticosteroids used in infiltration of joints Methylprednisolone, Triamcinolone, Betamethasone or Dexamethasone, for example, and its effect on the joint lasts between days to weeks.
3. Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is a component of synovial fluid, which is the natural lubricant that exists within the joints; however, in certain degenerative diseases, such as osteoarthritis, there may be a loss of this lubrication, which accounts for most of the symptoms.
In these cases, the physician can inject this acid into the joint, in a technique called viscosupplementation, which is capable of creating a protective film that delays the progression of wear and relieves pain.
Usually, the treatment consists of 1 application per week for 3 to 5 weeks, and although the effect is not immediate, being started gradually about 48 hours after the procedure, its results are much longer and can remain for several months. See the effects, contraindications and the price of hyaluronic acid injections.

How is it done?
The procedure of an infiltration is relatively simple but should only be performed by an experienced doctor in the doctor's office, requiring disinfection of the skin and use of sterile materials.
Initially, a local anesthetic is done and then the medicine is applied, which can be done with the aid of an ultrasound or radiography, to determine exactly the location. The complete procedure of a joint infiltration lasts for 2 to 5 minutes and although it causes some pain, it is slight and bearable.
After the procedure, complete recovery should occur in 1 to 2 weeks. Those who practice physical activity should not return to training in the first week, and if it is difficult to walk without limping, the doctor may suggest using crutches to avoid damaging the spine or other knee.
In addition, preferably after infiltration the person should continue to perform physiotherapy, hydrotherapy and muscle strengthening to strengthen muscles, improve movement of affected joints, decrease pain, increase elasticity and decrease the progression of arthrosis, thus avoiding placement of a prosthesis.
Side effects
After injection into the joint, it is common to have some swelling and pain, so it is recommended to rest to let the medicine work. The risk of infection also exists but is very low.
This procedure should be avoided by people using anticoagulant drugs, who have diseases that impair blood clotting in order to avoid the risk of bleeding, or by pregnant women and breastfeeding women. It should also not be performed on people with allergies or who have any infection in the area. In addition, it should be used cautiously in athletes because the corticoid and anesthetic can be detected in blood tests and are on the list of prohibited drugs.