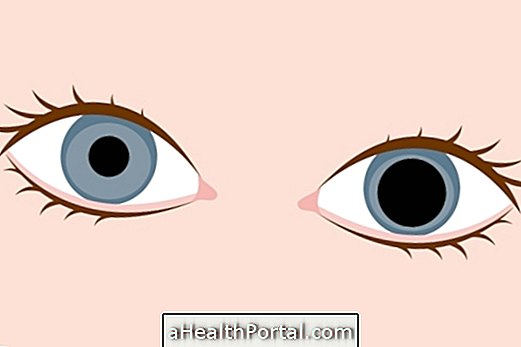
Adie's pupil is a rare syndrome in which one of the eye pupils is generally more dilated than the other, reacting very slowly to changes in light. Thus, it is common that in addition to the aesthetic change, the person also has symptoms such as blurred vision or sensitivity to light, for example.
In some cases, the pupil change may start in one eye, but over time, it may reach the other eye, worsening the symptoms.
Although there is no cure for Adie's pupil, the treatment can greatly reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life, and may be prescribed by the ophthalmologist to use grade glasses or the application of special eye drops.
See that other diseases can cause changes in pupil size.
Main symptoms
In addition to the presence of pupils of different sizes, Adie syndrome may cause other symptoms such as:
- Blurry vision;
- Hypersensitivity to light;
- Constant headache;
- Pain in the face.
In addition, people with Adie pupils usually also have weakening of the inner tendons, such as the knee, for example. Thus, it is common for the physician to test the hammer by tapping a small hammer in the region just below the knee. If the leg does not move or move slightly, it usually means that the deep tendons are not working properly.
Another very common feature of Adie's syndrome is the presence of excessive sweating, sometimes on only one side of the body.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of a rare syndrome such as Adie's pupil can be difficult because there is no test capable of confirming the disease. Thus, it is common for the doctor to evaluate all symptoms of the person, his medical history and the results of various tests, especially to disguise other more common diseases that may have similar symptoms.
Thus, it is quite common for various types of treatment to be tried before hitting the most appropriate treatment, since the diagnosis may vary over time.
What causes Adie's pupil
In most cases, Adie's pupil does not have a specific cause, but there are situations where the syndrome may arise due to an inflammation of the nerves behind the eye. This inflammation can be caused by an infection, by complications of eye surgery, by the presence of tumors, or by traumas due to traffic accidents, for example.
How is the treatment done?
In some cases, the Adie's pupil does not cause any discomfort to the person and therefore the treatment may not even be necessary. However, if there are symptoms that are causing discomfort the ophthalmologist can advise some forms of treatment such as:
- Use of lenses or degree glasses : helps to improve blurry vision, allowing better focus on what is being seen;
- Application of drops with Pilocarpine 1% : it is a medicine that contracts the pupil, reducing the symptoms of sensitivity to light, for example.
However, it is best to always consult an ophthalmologist, especially when there are changes in the pupil that need to be evaluated to know the best form of treatment.