The treatment of eclampsia consists of the administration of magnesium sulphate in the vein, ingestion of water and rest. In addition, it may be necessary to induce labor if the problem persists, and continue treatment on the following days.
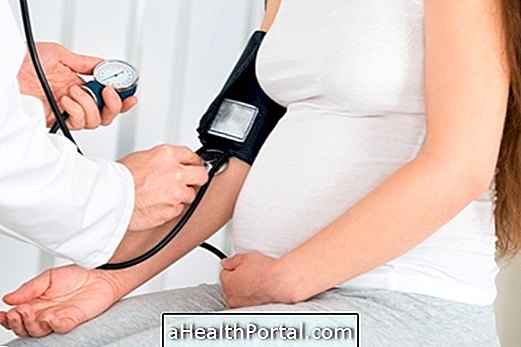
Eclampsia is a serious problem that occurs in pregnancy, which causes symptoms such as high blood pressure, swelling in the body, seizures and coma, and can be fatal if left untreated. This problem is more common in the last 3 months of pregnancy, however, it may manifest itself before this period, at delivery or postpartum. Learn more about eclampsia.
How is the treatment done?
Eclampsia, unlike common arterial hypertension, does not respond to diuretics or a diet low in salt, so the treatment consists of the following:
1. Administration of Magnesium Sulphate
The administration of magnesium sulphate in the vein is the most common treatment in cases of eclampsia, which acts to control seizures and coma. Treatment should be done after hospitalization and magnesium sulfate should be administered by a healthcare professional directly into the vein.
2. Rest
During hospital stay, the pregnant woman should rest as much as possible, preferably lying to the left side, in order to improve the blood flow to the baby.
3. Induction of childbirth
Childbirth is the only way to cure eclampsia, however induction can be delayed with medications so that the baby can develop as much as possible.
Thus, during clinical treatment, a clinical examination should be performed daily, every 6 hours to monitor the progression of eclampsia, and if there is no improvement, labor should be induced as soon as possible in order to resolve the convulsions by eclampsia.
Although eclampsia usually improves after childbirth, complications can occur on the following days, so a woman should be monitored closely and when signs of eclampsia persist, hospitalization may last from a few days to weeks, depending on the severity of the problem and complications.