Hypoxia is the decrease in the supply of oxygen to the tissues of the body. The lack of oxygen in the blood, which can also be called hypoxemia, is a serious condition, which can lead to serious tissue damage and, consequently, the risk of death.
The brain is a very impaired organ in this situation because its cells can die in about 5 minutes because of lack of oxygen, so whenever signs of hypoxia are identified, such as shortness of breath, mental confusion, dizziness, fainting, coma or it is important to go to the emergency room as soon as possible.
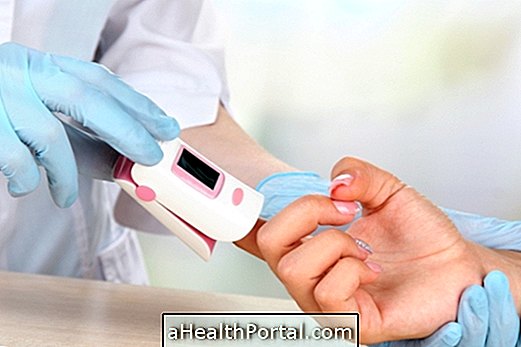
To identify the lack of oxygen in the blood, the doctor can identify the signs through the physical examination and request tests such as pulse oximetry or arterial blood gases, for example, that can identify the concentration of oxygen in the bloodstream. Learn more about exams that identify hypoxia.
What can cause hypoxia
The lack of oxygen in the blood and tissues can have different causes, which include:
1. Hypnoxia by altitude or "Evil of heights"
It arises when the amount of oxygen in the air breathed is not enough, which usually happens in places with altitudes higher than 3, 000 meters, since the further away from sea level, the lower the concentration of oxygen in the air.
2. Pulmonary diseases
Changes in the lungs caused by diseases such as asthma, emphysema, pneumonia or acute pulmonary edema, for example, hinder the entry of oxygen through their membranes into the bloodstream, reducing the amount of oxygen in the body.
There are also other types of situations that prevent breathing, such as due to neurological diseases or coma, in which the lungs can not do their job properly.
3. Changes in blood
Anemia, caused by lack of iron or vitamins, bleeding, or genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia can cause lack of oxygen in the body, even if breathing functions normally.
This is because anemias cause insufficient amounts of hemoglobin, which is a protein present in the red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen captured in the lungs and delivered to the tissues of the body.
4. Poor blood circulation
It happens when the amount of oxygen is sufficient in the blood, however, the blood can not reach the tissues of the body due to an obstruction, as it happens in the infarction, or when circulation in the bloodstream is weak, caused by heart failure, for example.
5. Intoxication
Situations such as carbon monoxide poisoning or poisoning by certain drugs, cyanide, alcohol, or psychoactive substances can prevent the oxygen binding to hemoglobin or prevent the oxygen uptake by tissues, and therefore can cause hypoxia.

6. Neonatal hypoxia
Neonatal hypoxia occurs due to deficiency of oxygen supply to the baby through the maternal placenta, causing fetal distress.
It can occur before or during childbirth due to changes in the mother's blood circulation, high blood pressure, thrombosis or placental abruption, for example, and should be promptly treated by the obstetrician and neonatologist to prevent damage to the organs, especially the brain, and sequelae to the baby. Find out what are the changes in the placenta that can harm the baby.
What are the symptoms
Symptoms that indicate lack of oxygen in the blood are:
- Shortness of breath;
- Accelerated breathing;
- Palpitations;
- Irritation;
- Dizziness;
- Excessive sweating;
- Mental confusion;
- Somnolence;
- Fainting;
- Cyanosis, which are the ends of the fingers or purplish lips;
- With the.
However, when the lack of oxygen is located in only one organ or region of the body, specific lesions are caused in that tissue, which is called ischemia or infarction. Some examples of this situation are heart attack, intestinal, pulmonary or stroke, for example.
In addition, lesions caused in the tissues by the lack of oxygen can be reversible, after the correction of this problem and recovery of the cells, however, in some cases, the lack of oxygen causes tissue death, causing permanent sequelae. Find out what are the main sequelae that can occur after a stroke.
What to do in case of hypoxia
The treatment for lack of oxygen is usually initiated with the use of oxygen mask to seek to normalize their blood levels, however, the situation will only really be dealt with by the resolution of the cause of hypoxia.
Thus, depending on the cause, specific treatments such as antibiotic use for pneumonia, nebulization for asthma, medicines to improve the functioning of the lungs or heart, treatments for anemia or antidotes for poisonings, for example, are indicated by the doctor.
In severe cases, which are caused by brain damage or can not be resolved immediately, artificial respiration may be necessary through devices in the ICU setting and with the use of sedative medications until the physician is able to stabilize the capacity respiratory. Understand when induced coma is necessary.