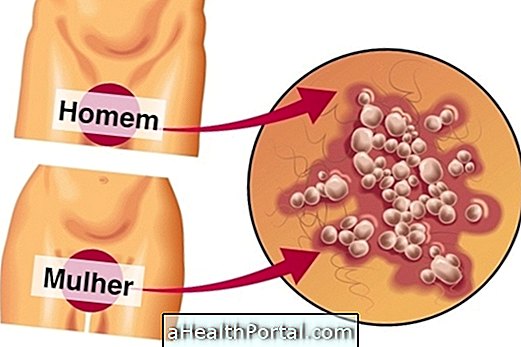
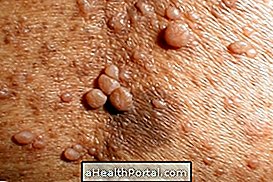
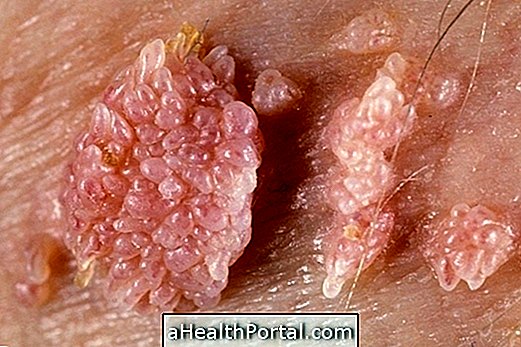
The appearance of several small warts with a small ridge in the intimate region of the male or female is the main symptom of HPV. These warts can appear weeks, months or years after being contaminated with the virus.
Typically, HPV-like warts appear in the male or female genital region or even in the mouth, affecting the throat or tongue. The incubation period of the HPV virus is usually 3 to 4 months, but can take up to 2 years to manifest.
However, in most cases HPV does not show any symptoms, although the infected person may already contaminate others. The most common one is to only find out that you have HPV through microscopic examination. Whenever a person has HPV, their sexual partner should be examined because they may also be infected, and there is a greater risk of developing cancer where the virus is.
Symptoms of HPV in man
The symptoms of HPV in man include the presence of several warts of varying sizes in the male genital area, such as in the penis, scrotum, or anus, these warts may be so close together that they form plaques.
However, man, despite being infected with the HPV virus, may show no symptoms, although he may transmit the disease to others through intimate contact without a condom. Learn more at: HPV in man.
Symptoms of HPV in women
HPV symptoms in women include the presence of various warts of varying sizes on the vulva, large or small labia, vaginal wall, cervix or anus, and as in man, they may be so close together that they form plaques.
In addition to warts visible to the naked eye, symptoms such as burning, itching or vaginal discharge may also occur.


Symptoms of HPV in the mouth and throat
The symptoms of HPV in the mouth include several small warts of varying sizes that can be on the lips, cheeks, tongue, sky of the mouth or throat.
HPV warts can occur at these locations when this region contacts the genitals of a person who has the HPV virus during oral sex, for example.
Learn more about HPV in the mouth.
How to know if I have HPV
The diagnosis of HPV can be made through clinical-visual examination, but in some cases, when the warts are very small, exams such as colposcopy and acetic acid application may be needed to see the warts.
In women, HPV-related cervical lesions can be detected by a cervical or anal smear, performed by the gynecologist.
What is the treatment for HPV?
The treatment for HPV is to use specific ointments daily from 6 months to 2 years. Some HPV lesions can still be treated with the use of cauterization or laser, and the gynecologist is the one who decides which treatment is most appropriate. See also: Treatment of HPV.
See how to identify, how the transmission is and how to treat HPV by watching the following video: